Figure 1.
Spatial Receptive Fields in the Mouse SCN
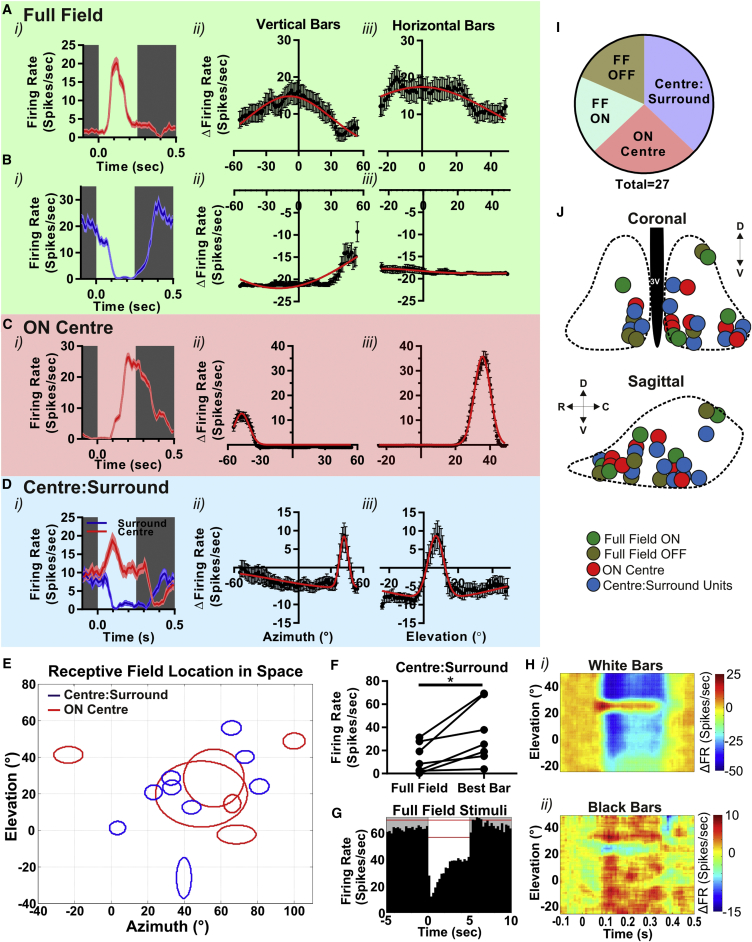
(A–D) Responses to the receptive field mapping protocol of single units representative of full-field ON (A), full-field OFF (B), ON center (C), and center:surround (D) response types. In each case, the panel to left (i) shows modulation in firing rate (10-ms bins with a five-bin boxcar average; mean ± SEM) associated with the appearance of a white bar between time 0 and 0.25 s at the location eliciting maximum response (or for center:surround maximum excitation [red] and inhibition [blue]); the center and right panels are the mean ± SEM change firing from baseline (relative to preceding 100 ms) following appearance of vertical (ii) or horizontal (iii) bars as a function of location on azimuth or elevation of bar center (0° corresponds to point directly in front of center of eye). Red lines depict difference of Gaussian fit.
(E) Projection of RFs for ON center (red) and center:surround (blue) responses in visual space (0° corresponds to point directly in front of center of eye).
(F) Comparison of firing rates for ten center:surround units under full white screen (full field) or a white bar at preferred spatial location (“best bar”; paired t test; p < 0.05).
(G) Change in mean firing rate (250-ms bins; red lines denote 99% confidence interval for baseline firing) to a full screen irradiance increment (time 0–5 s) for a representative center:surround unit inhibited by full-field stimulus.
(H) Heatmaps showing firing rate (scale to right) of a representative center:surround unit when presented (time 0–0.25 s) with either white bars against a black background (i) or black bars against a white background (ii) at various elevations.
(I) Pie chart depicting the proportion of single units that display each of the RF types (“FF” denotes full field; n = 27 cells from 11 mice).
(J) Approximate anatomical location of recording sites at which units with each RF type were recorded superimposed upon schematic of the SCN in coronal (above) and sagittal (below) projection. Dotted lines represent boundaries of SCN; 3V, 3rd; C, caudal; D, dorsal; R, rostral; V, ventral.
See also Figure S1.