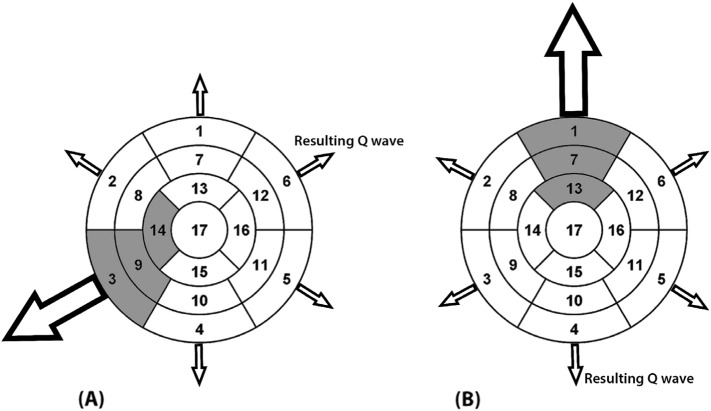
Fig. 1.
Pathogenesis of Q waves in HCM patients. Based on our results, abnormal Q waves may be generated by an increased electrical force generated by hypertrophied LV wall overpowering the electrical vector by its opposite wall nearest to the exploring lead. 1: basal anterior, 2: basal anteroseptal, 3: basal inferoseptal, 4: basal inferior, 5: basal inferolateral, 6: basal anterolateral, 7:mid anterior, 8: mid anteroseptal, 9: mid inferoseptal, 10: mid inferior, 11: mid inferolateral, 12: mid anterolateral, 13: apical anterior, 14: apical septal, 15:apical inferior, 16: apical lateral, 17: apex. The shaded segments: hypertrophied segments. The arrow size is proportionate to electrical forces generated by the corresponding ventricular walls. A: increased DT ratio Inferior Septum/Lateral wall, B: Increased DT ratio Anterior/Inferior wall.