Figure 1.
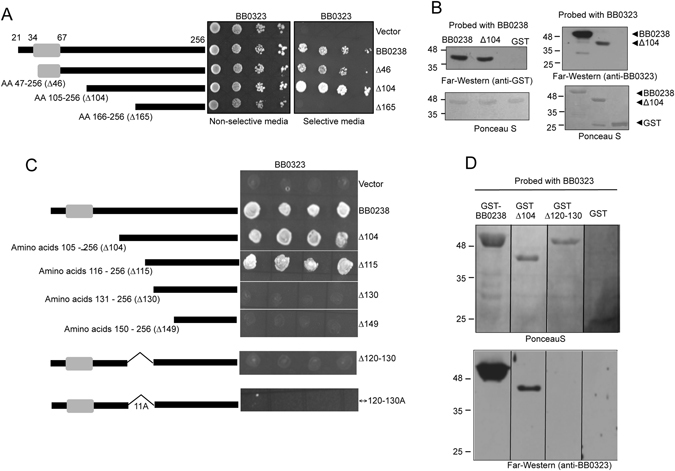
Probing the BB0238-BB0323 interaction. (A) Residues 34–67 in BB0238 are not involved in the interaction with BB0323. Yeast two-hybrid assays for assessment of BB0238-BB0323 interaction. The yeast vector pGAD expressing GAL4 activation domain (AD) or various fusions of AD-BB0238 were introduced into yeast along with the vector pGBKT7 expressing the GAL4 DNA binding domain (BD) fused with BB0323. Serially diluted transformants were grown in non-selective (SD-Trp-Leu) or selective (SD–Ade–His–Leu–Trp) media and yeast growth was recorded. (B) BB0323 and BB0238 interact in Far-Western assays. Recombinant BB0323 (left panels) or BB0238 (right panels) was subjected to SDS-PAGE and incubated with glutathione S-transferase (GST)-fused BB0238, or His-tagged BB0323 proteins, and binding was examined by appropriate primary and secondary detection antibodies. (C) Residues 120–130 of BB0238 mediate the interaction with BB0323. Yeast vector expressing indicated AD-BB0238 fusion proteins were cotransformed with BD-BB0323 and growth was assessed, as detailed in panel A. (D) BB0238 missing 11-residue interaction motif failed to bind BB0323 in far-Western assays. Recombinant GST-BB0238 fusion proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE and incubated with recombinant his-tagged BB0323 and the interaction was monitored as described in panel B. Migration of protein standards is shown to the left in kilodaltons.
