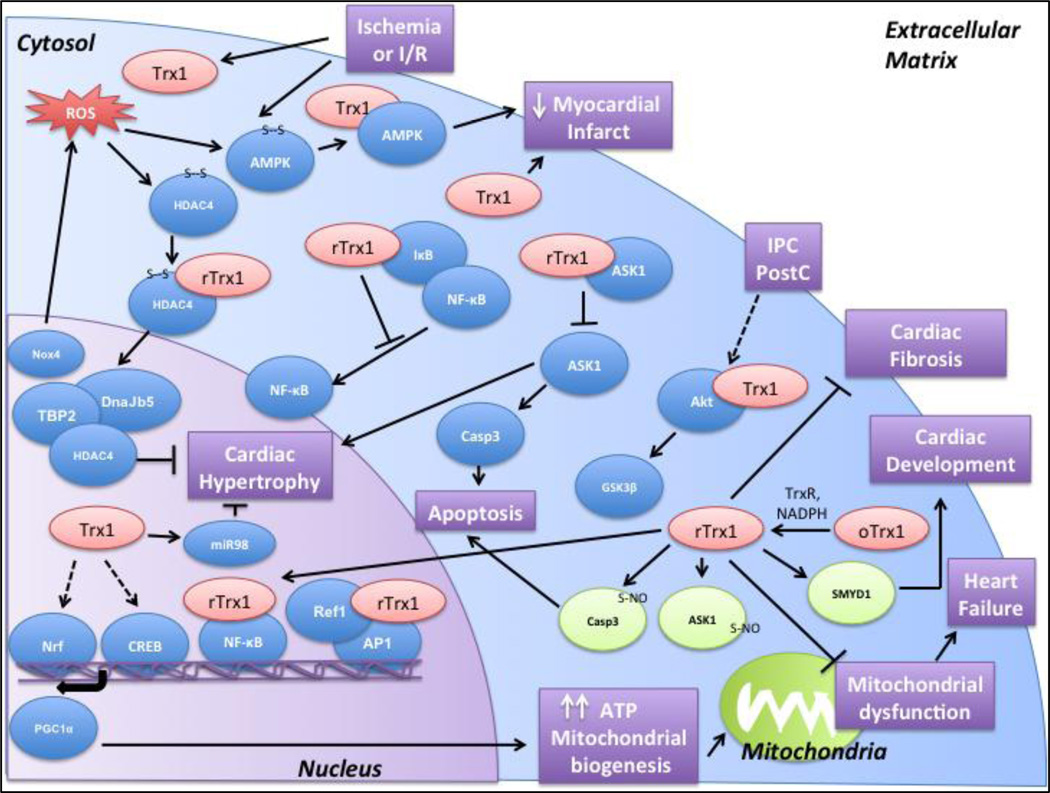
Figure 2.
Trx1 binds to its targets and exerts cardioprotection by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction, increasing ATP production and mitochondrial biogenesis, inhibiting apoptosis, and preventing cardiac hypertrophy and cardiac fibrosis. It mainly interacts with and reduces disulfide bonds in its target molecules. It can also participate in other post-translational modifications such as S-nitrosylation and methylation (indicated in green). The functional significance of Trx1 in the heart is highlighted in purple. (Abbreviations: ROS- Reactive Oxygen Species, I/R- Ischemia/Reperfusion, IPC- Ischemic Preconditioning, Post-Postconditioning)