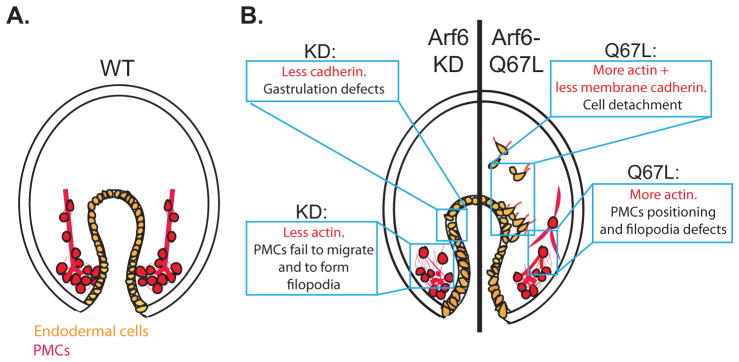
Fig. 7. Model of Arf6 functions in the embryo.
(A) The gut of the WT gastrulae consists of a single layer of endodermally-derived epithelial cells that adhere to each other in an organized pattern (orange). The PMCs (red) migrated anteriorly and produced skeleton rods (red line) within their filopodial cables. (B) Arf6 perturbed embryos result in endodermal and skeletogenesis defects. Arf6 KD gastrula (left side of the embryo) has gastrulation defects, possibly due to the decrease of the junctional cadherin of the endodermal cells. Arf6 KD gastrula also has clumped PMCs that fail to migrate anteriorly, potentially due to decreased Arf6 that remodel actin. Gastrula injected with Arf6-Q67L mRNA (right side of the embryo) has detached endodermal cells, potentially due to the increase in actin remodeling and decrease in the levels of membrane cadherin, which may promote EMT of the endodermal cells. PMCs in the gastrula injected with Arf6-Q67L mRNA are connected by extensive thick filopodia that may interfere with the proper skeletogenesis, potentially due to the excessive actin remodeling.