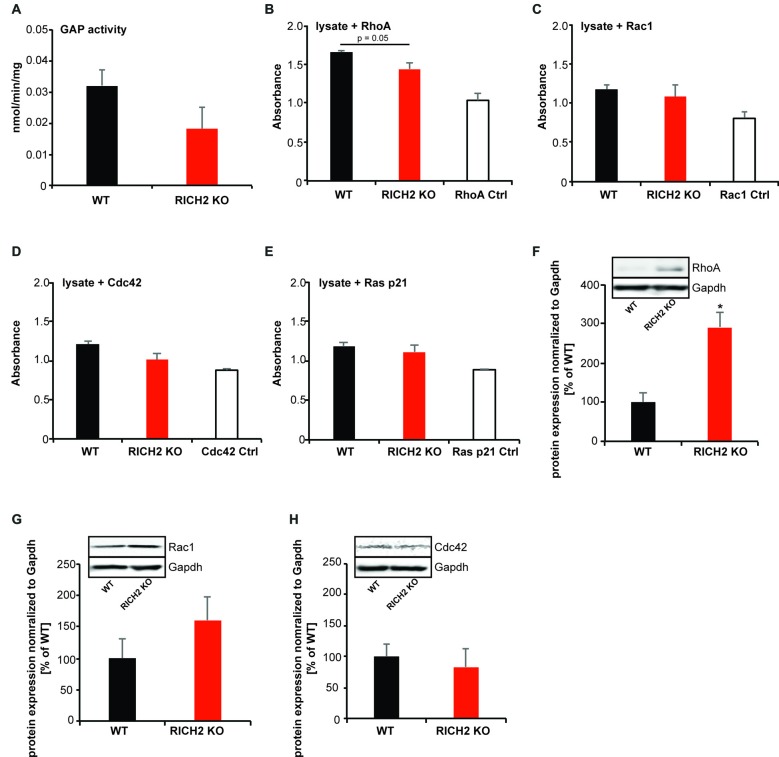
Figure 5.
Altered Rho GTPase signaling in amygdala of RICH2 KO mice. (A) Comparison between the GTPase activating protein (GAP) activity of the P2 lysates from WT and RICH2 KO mice. The GAP activity is measured in nmoles/min/mg of small G-protein. First a standard curve is made using the absorbance of KH2PO4 at different concentrations, later the absorbance of WT and RICH2 KO lysates are plotted on the graph. The GAP activity is higher for WT lysates compared to RICH2 KO lysates. (B) In the presence of the small G protein RhoA, the absorbance of WT lysates is higher than that of RICH2 KO lysate, which indicates that RICH2 is acting as a GAP for RhoA in amygdala. (C) There is no difference between the absorbance of WT and RICH2 KO lysates in the presence of RAC1 and CDC42 (D,E) Like RAC1 and CDC42, RAS p21 is not a target G protein for RICH2 in amygdala as there is no difference in the absorbance of WT and RICH2 KO lysates in the presence of RAS p21. (F) Western blot analysis of amygdala P2 lysates reveals that expression of RhoA is significantly higher in RICH2 KO lysates, in comparison with WT lysates (Unpaired t-test, p = 0.0508, n = 3). (G,H) Western blot analysis revealed no alteration in the expressions of Rac1 (G) and Cdc42 (H) between WT and RICH2 KO using amygdala P2 lysates.