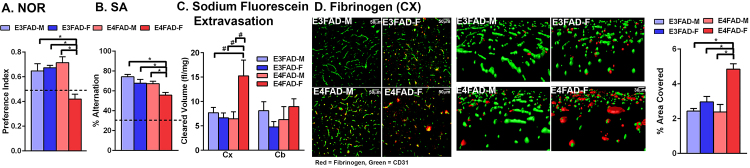
Fig. 1.
Cognitive and cerebrovascular dysfunction in E4FAD-F mice. E4FAD-F mice are cognitively impaired compared to E3FAD-M mice, E3FAD-F and E4FAD-M mice, when assessed by novel object recognition (NOR; A.) and spontaneous alternation (SA; B.). The dashed line in A. represents no preference and in B. chance alternation. C. After intraperitoneal injection, levels of sodium fluorescein are higher in the cortex (CX) of E4FAD-F mice compared to E3FAD-M mice, E3FAD-F or E4FAD-M. Cleared volume represents the levels of sodium fluorescein in the brain after normalization to plasma levels and brain weight. D. Levels of the plasma protein fibrinogen are higher in the cortex when assessed by quantitative immunohistochemical analysis. Representative confocal images from the cortex highlight the higher levels of fibrinbogen (red) in the cortex, and also indicate lower vessel coverage (CD31 green) in E4FAD-F mice compared to all groups. n = 7 (E3FAD-M), 6 (E3FAD-F), 6 (E4FAD-M), 8 (E4FAD-F). Data expressed as mean +/− S.E.M. *p < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc comparisons. #p < 0.05 by two-way AVOVA followed Fisher’s LSD test.