Figure 4.
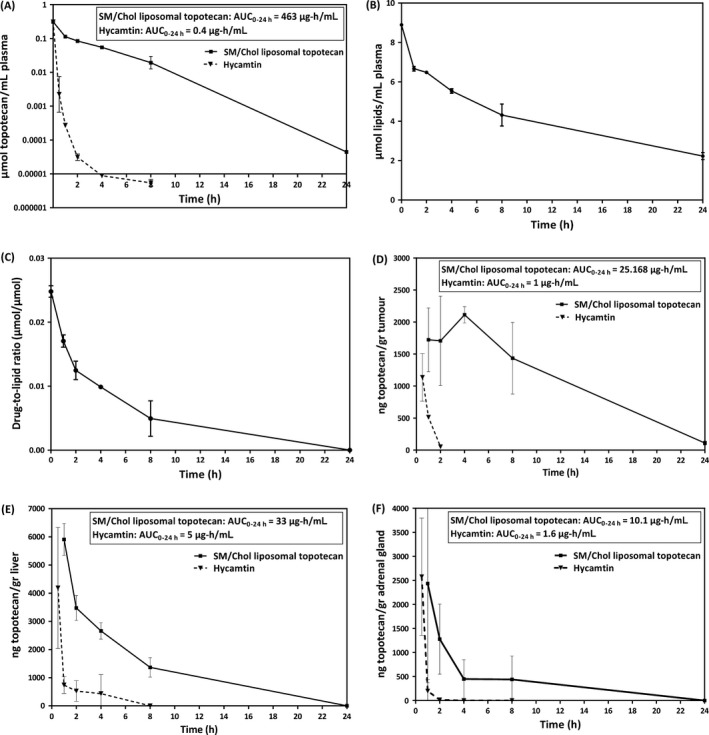
Administration of SM/Chol liposomal topotecan, in comparison to Hycamtin, enhances drug exposure in the plasma compartment, tumor, liver and adrenal gland. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution were assessed after a single 5 mg/kg dose of topotecan administered as the SM/Chol liposomal formulation or Hycamtin. Formulations were administered i.v. into NRG mice with established s.c. LAN‐1 tumors. Plasma topotecan levels following administration of Hycamtin (panel A, filled triangles) and SM/Chol liposomal topotecan (panel A, filled squares) were determined by HPLC analysis as described in the Methods. Plasma liposomal lipid levels following administration of SM/Chol liposomal topotecan is shown in panel B, where liposomal lipid was measured using 3H‐CHE as a liposomal lipid marker by liquid scintillation counting (LSC). The calculated change in drug‐to‐lipid ratio in the plasma compartment following administration of SM/Chol liposomal topotecan is shown in panel C. Topotecan levels in tumor, liver and adrenal gland after administration of Hycamtin or the SM/Chol liposomal topotecan formulation are shown in panel D, E and F, respectively. Data points represent mean ± SEM obtained using at least three animals per group.
