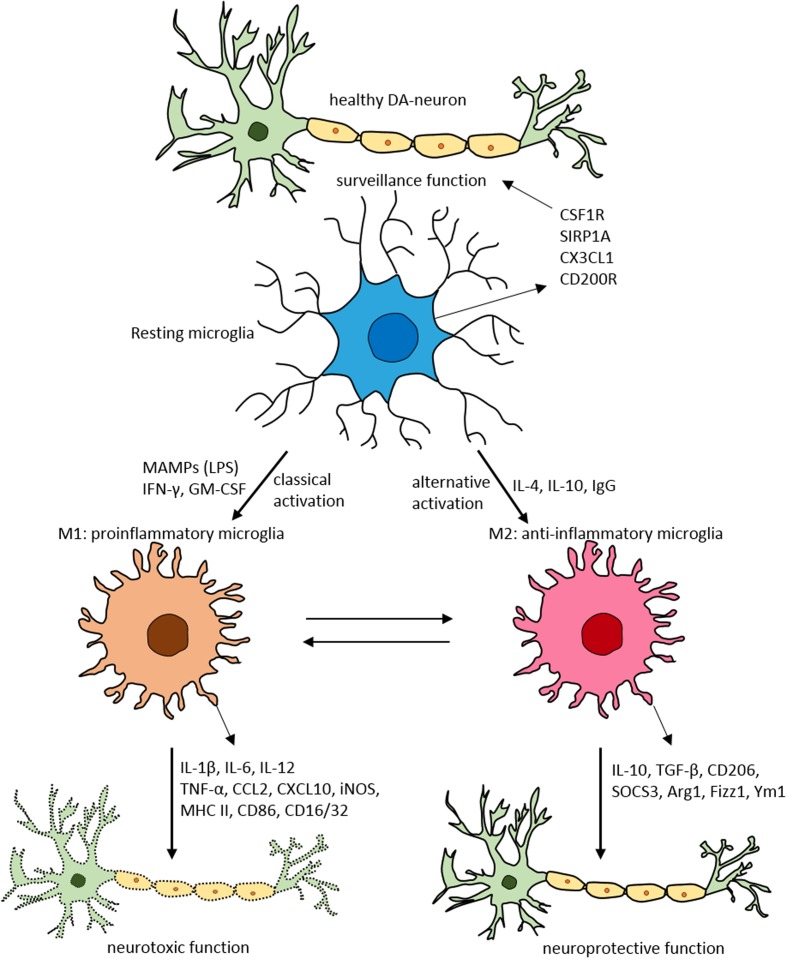
FIGURE 2.
Schematic of microglial polarization states and function. In normal physiological conditions microglia acquire the surveillance phenotype to maintain all CNS cell types including neurons. To maintain this surveillance state, microglia secrete several factors including colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R), signal regulatory protein CD172 (SIRP1A), chemokine CX3CL1 and CD200R. Upon classical activation when triggered by LPS, IFN-γ, or GM-CSF microglia acquire M1 pro-inflammatory phenotype leading to neurotoxicity by secreting several pro-inflammatory substances (for detailed list, see Table 1). When activated alternatively by IL-1, IgG, or IL-10 microglia attain M2 anti-inflammatory state prompting neuroprotection through secretion of variety of substances (for detailed list, see Table 1). Arg1, arginase 1; CCL, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand; CD, cluster of differentiation; CSF1R, colony stimulating factor 1 receptor; CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; Fizz1, found in inflammatory zone; IL, interleukin; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MAMPs, microbe-associated molecular patterns; MHC-II, major histocompatibility complex II; SIRP1A, signal regulatory protein CD172; SOCS3, suppressor of cytokine signaling-3; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; Ym1, chitinase-like protein.