Fig. 5.
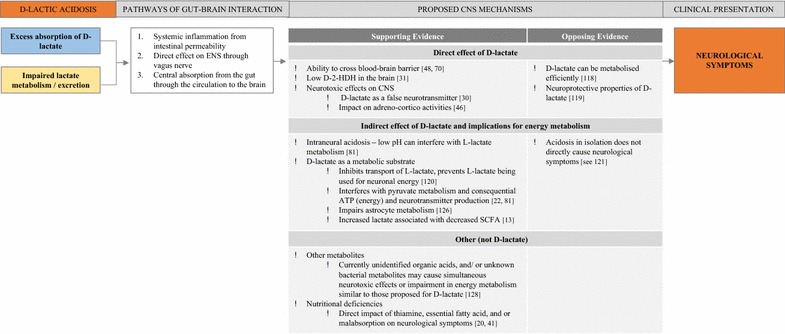
Proposed mechanisms of gut–brain interaction leading to neurological symptoms observed in d-lactic acidosis. Supporting and opposing evidence for proposed central nervous system (CNS) mechanisms are categorised according to direct effects of d-lactate, indirect effects of d-lactate and other possible mechanisms unrelated to d-lactate. Abbreviations: enteric nervous system (ENS); d-2-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase (d-2-HDH); adenosine triphosphate (ATP); short chain fatty acids (SCFA)
