Fig. 4.
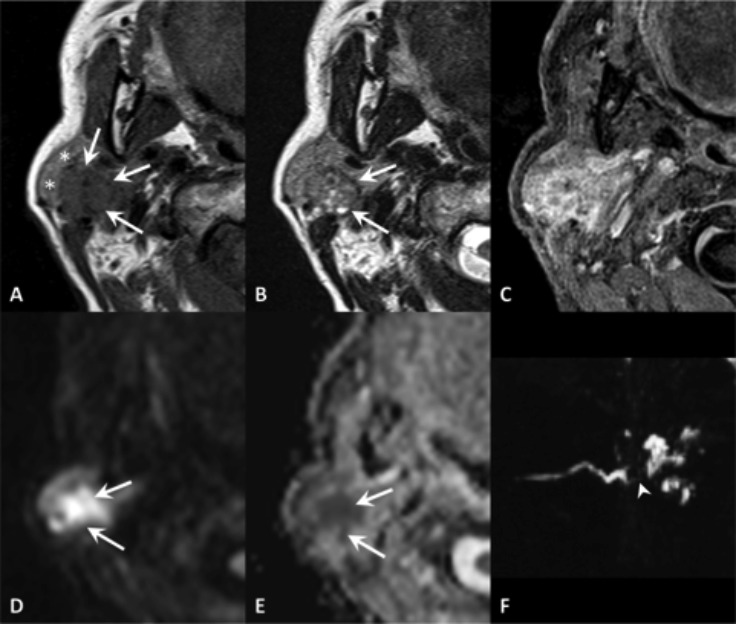
Focal obstructive sialadenitis. MR axial SE T1 (A), TSE T2 (B), VIBE after contrast administration (C), DWI b1000 (D) with ADC map (E); sialo-MR (maximum intensity projection in the sagittal plane) (F). Sudden onset of painful swelling of the right parotid gland. The focal inflamed area (arrows) can be detected because of its mass-effect on the adjacent gland tissue (asterisks), greater post-contrast enhancement and diffusion restriction. The MR sialography shows a filling defect (arrowhead) and intraglandular duct ectasia.
