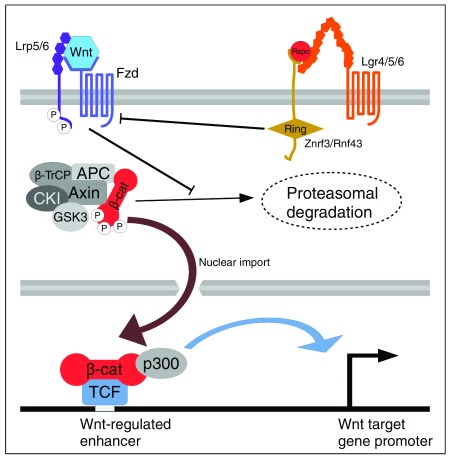
Figure 1. Overview of vertebrate Wnt/β-catenin (Wnt/β-cat) signaling.
Wnt binding to Frizzled (Fzd) and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6 (Lrp5/6) co-receptors promotes the phosphorylation of Lrp5/6’s cytoplasmic tail. These interactions block the ability of the destruction complex to phosphorylate and ubiquitinate β-cat, preventing its degradation by the proteasome. Stabilized β-cat enters the nucleus, where it is recruited to Wnt-regulated enhancers by transcription factors (TFs) of the T-cell factor (TCF) family. R-spondin (Rspo) potentiates Wnt/β-cat signaling by increasing the number of Fzd receptors. Rspo forms a complex with Lgr4/5/6 and zinc and ring finger 3 (Znrf3)/ring finger protein 43 (Rnf43), preventing the latter from ubiquitinating Fzd receptors. APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; CKI, casein kinase I; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase 3; β-TrCP, β-transducin repeat-containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase.