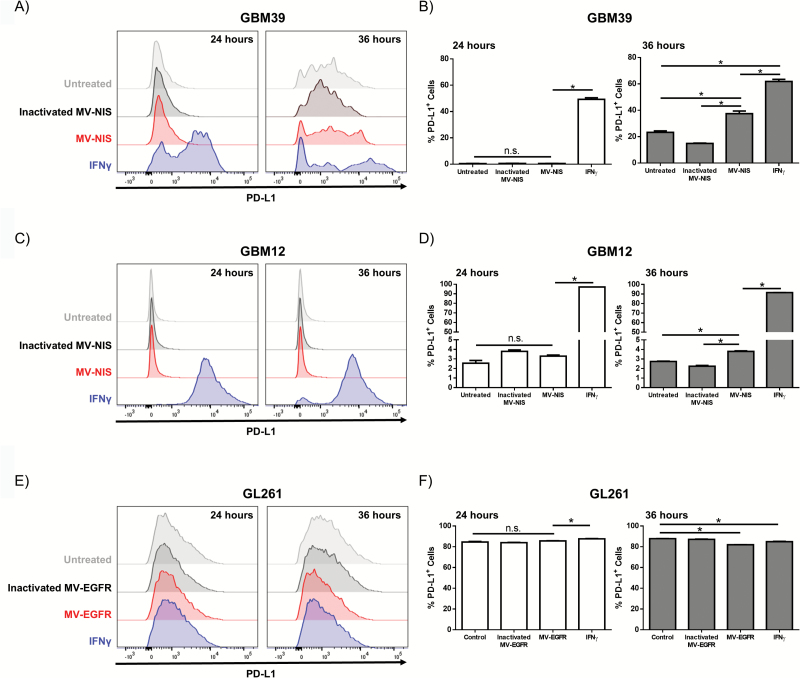
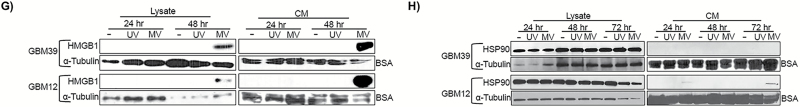
Fig. 1.
In vitro IFN-γ treatment or MV infection of GBM cells modulates expression of PD-L1. Human GBM39 (A‒B), GBM12 (C‒D), or murine GL261 (E‒F) were treated with MV, inactivated MV, or IFN-γ and assessed for PD-L1 expression by flow cytometry 24 and 36 hours post treatment (N=2 per treatment). (A, C) Representative flow cytometry histograms and (B, D) quantification of PD-L1 expression demonstrate that IFN-γ increases PD-L1 expression on GBM39 cells and GBM12 cells. (E) Representative histograms and (F) quantification demonstrate that the GL261 glioma cell line expresses high levels of PD-L1 independent of treatment. Error bars represent mean±SEM. * denotes P<.05. Expression of HMBG1 and HSP90 by western immunoblotting in untreated (-), UV-MV-NIS (UV), and MV-NIS treated GBM39 and GBM12 cells at the indicated time points post-infection: increased expression of HMGB1 was detected both in lysates and CM at 48 hours (G); increased expression of HSP90 was only detected in CM of GBM12 cells (H).