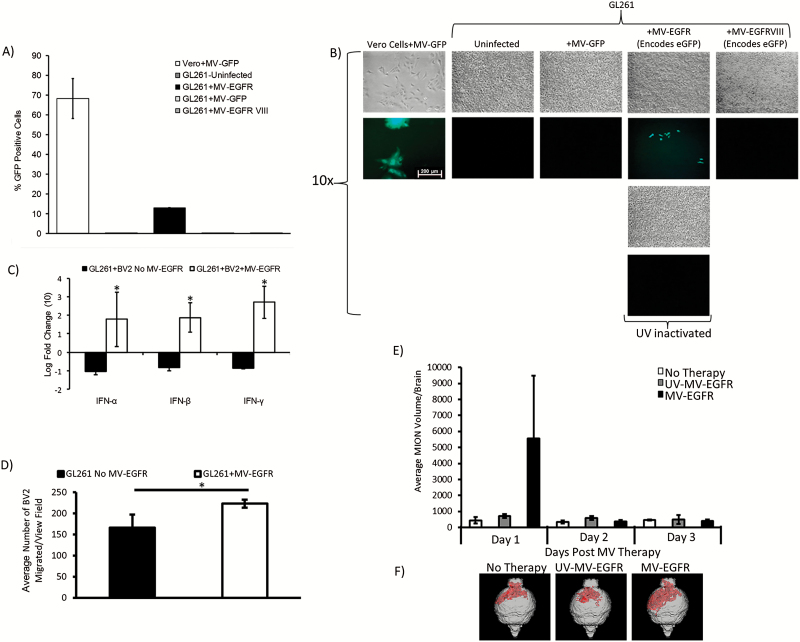
Fig. 2.
MV-EGFR infection of murine GL261 glioma cells is limited, but stimulates pro-inflammatory responses in vitro and in vivo. (A) GFP FACS quantification in MV infected GL261 cells. (B) GFP detection by fluorescence microscopy pictures 3 days post infection of GL261 with MV or corresponding UV inactivated constructs (MOI = 3, scale bar = 200 µm). (C) Results of qRT-PCR of BV2 cocultures with MV-EGFR infected GL261 cells. IFN-α, IFN-β, and IFN-γ were significantly upregulated compared with uninfected GL261 cells (*P<.05). (D) MV-EGFR infection of GL261 cells significantly increased BV2 transwell migration (*P<.05) (E) Average MION volume from T2 weighted MRI of orthotopic GL261 tumors treated with MV-EGFR, UV-MV-EGFR, or untreated (n=3/group). Increased MION volume (monocytic infiltration) into the brains of MV-EGFR treated mice was observed one day post therapy. (F) Representative MION MRI reconstructions (red shading = MION+).