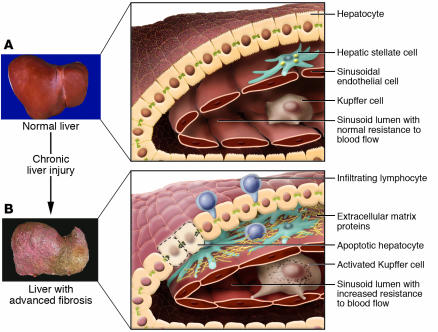
Figure 1.
Changes in the hepatic architecture (A) associated with advanced hepatic fibrosis (B). Following chronic liver injury, inflammatory lymphocytes infiltrate the hepatic parenchyma. Some hepatocytes undergo apoptosis, and Kupffer cells activate, releasing fibrogenic mediators. HSCs proliferate and undergo a dramatic phenotypical activation, secreting large amounts of extracellular matrix proteins. Sinusoidal endothelial cells lose their fenestrations, and the tonic contraction of HSCs causes increased resistance to blood flow in the hepatic sinusoid. Figure modified with permission from Science & Medicine (S28).