Figure 4.
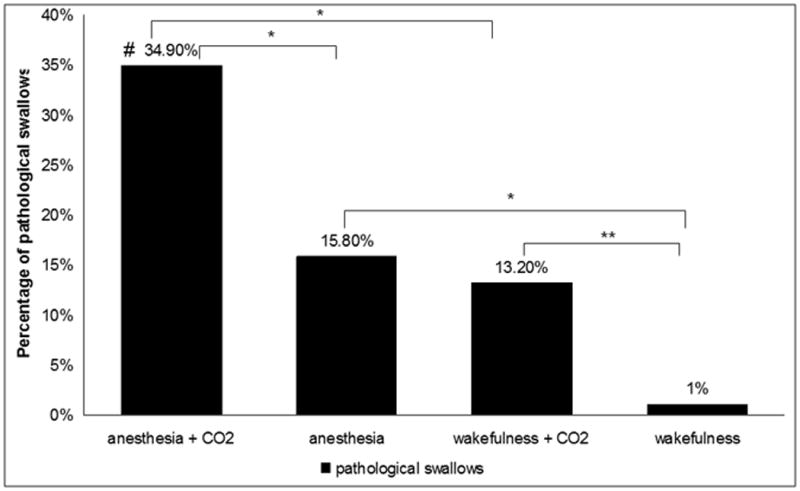
Proportion of pathological (inspiratory) swallows during wakefulness and anesthesia with and without evoked hypercapnia. Carbon dioxide (CO2) induces an increase in the proportion of pathological swallows during wakefulness and anesthesia. Anesthesia augmented the effects of carbon dioxide to impair breathing-swallowing coordination compared with wakefulness * indicates p<0.05, ** indicates p<0.001 # indicates interaction effect between anesthesia and carbon dioxide, p<0.05
