Figure 5.
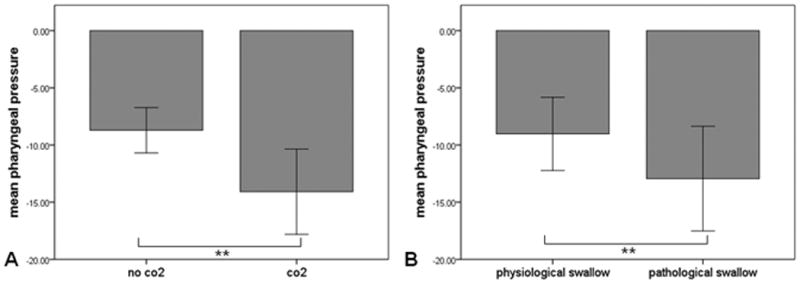
Association between hypercapnia, pharyngeal pressure during inspiration, and pathological swallows. A. Carbon dioxide (CO2 ) insufflation increases the pharyngeal pressure generated during inspiration. B. Increased pharyngeal pressure is associated with occurrence of pathological swallows. Error bars represent ± 1 standard deviation. ** p<0.001
