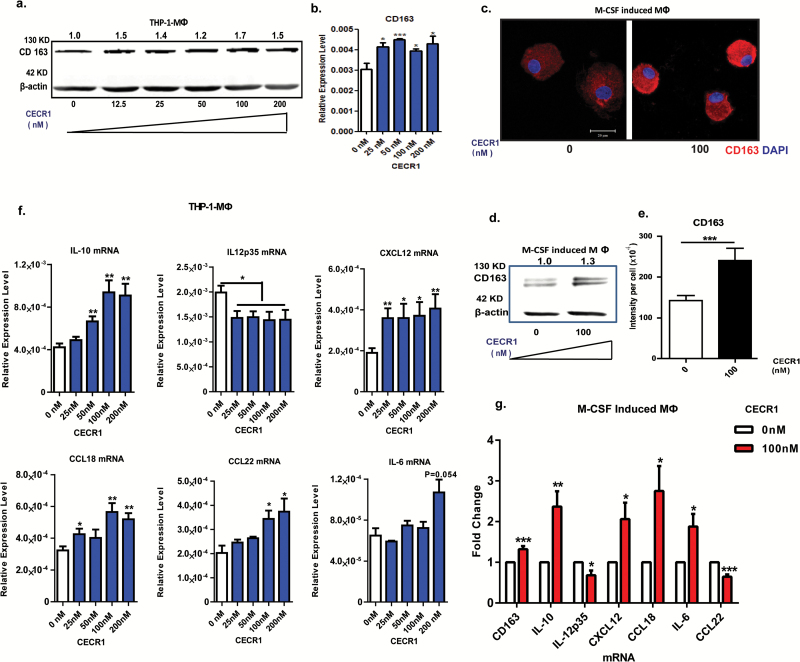
Fig. 3.
CECR1 promotes macrophages towards a M2-like phenotype. (A) Western blot of CD163 in THP-1 derived macrophages treated with rhCECR1 for 96 hours. Numbers above bands indicate quantified protein levels normalized to β-actin. (B) Quantitative PCR analysis of CD163 expression in THP-1 macrophages treated with rhCECR1. Data are from 3 experiments, normalized to β-actin, presented as mean ± SEM; *P < .05, ***P < .005. (C) Representative CD163 immunostaining of M-CSF induced macrophages with or without stimulation with CECR1 (100 nM) for 96 hours. Experiments were repeated 3 times independently (scale bar: 100 µm). (D) Representative western blot of CD163 in M-CSF induced macrophages with or without CECR1 stimulation for 96 hours from 3 experiments. Numbers above bands indicate quantified protein normalized to β-actin. (E) Quantified CD163 intensity in M-CSF induced macrophages with or without CECR1 (100 nM) stimulation is shown in mean ± SEM; ***P < .005. (F) Quantitative PCR analysis of M2-macrophage associated genes; IL-10, CXCL12, CCL18, CCL22, IL-6, and inflammatory gene IL-12p35 in THP-1 derived macrophages treated with CECR1 for 96 hours. Data normalized to β-actin are from 3 independent experiments and shown as mean ± SEM; *P < .05, **P < .01. (G) Quantitative PCR analysis of IL-10, CXCL12, CCL18, IL-6, IL-12p35, and CCL22 in M-CSF induced macrophages treated by CECR1(100 nM) for 96 hours. Data are from 3 experiments and shown as mean ± SEM in fold change compared with the CECR1 free condition. *P < .05, **P < .01.