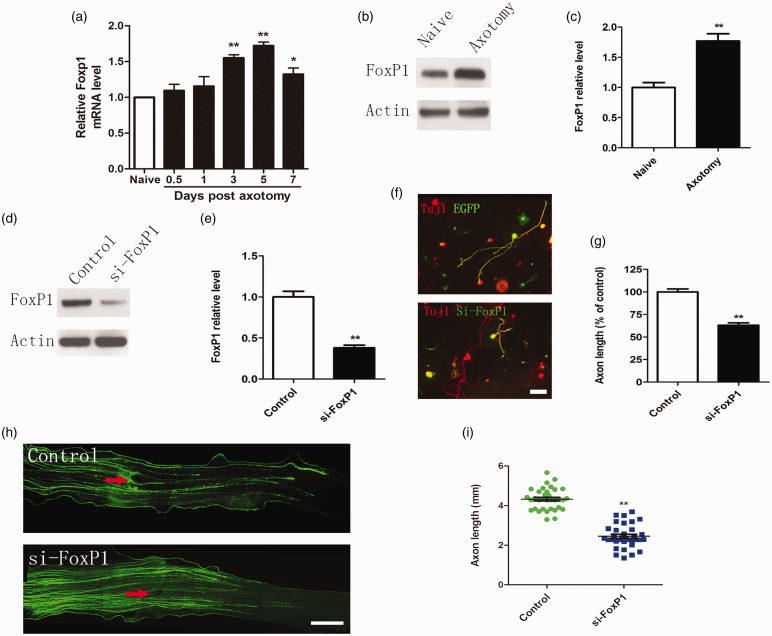
Figure 3.
FoxP1 regulates sensory axon regeneration. (a) qRT-PCR data indicating Foxp1 levels in adult dorsal root ganglions (DRGs) after sciatic nerve injury. Note that FoxP1 expression was significantly up-regulated from three to seven days after sciatic nerve axotomy (n = 3 for each condition). Error bars represent SEM. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. (b) Representative Western blot images of FoxP1 in adult DRGs seven days after sciatic nerve axotomy. (c) Quantification of FoxP1 protein level (normalized to actin, n = 3 for each condition). Error bars represent SEM. **P < 0.01. (d) Representative Western blot images of FoxP1 in cultured adult sensory neurons three days after transfection of FoxP1 siRNA oligos (siFoxP1). Note that transfection of siFoxP1 markedly knocked down FoxP1 protein level. (e) Quantification of FoxP1 level (normalized to actin, n = 3 for each condition). Error bars represent SEM. **P < 0.01. (f) Representative images of cultured adult sensory neurons expressing EGFP, EGFP + FoxP1 siRNA (siFoxP1). All neurons were stained with anti-β III tubulin antibody. Red: Tuj1; Green: EGFP. Scale bar = 100 µm. (g) Quantification of the average length of the longest axons (normalized to the average length of the control axons, n = 3). Error bars represent SEM. **P < 0.01. (h) Representative images of EGFP-labeled regenerating axons in the whole-mount sciatic nerves. Red arrowheads mark the crush sites. Bar = 500 µm. (i) Scatter plot of average lengths of regenerating sciatic nerve axons (n = 6 mice for each condition). Error bars represent SEM. **P < 0.01.