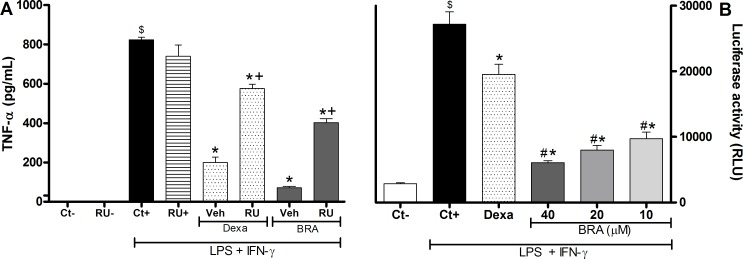
Fig 6. Involvement of glucocorticoid receptors and NF-κB dependent transcriptional activity in the immunomodulatory effect of braylin.
Panel A shows data from glucocorticoid receptor antagonism assay. Concentrations of TNF-α were determined in J774 macrophages treated with vehicle (50% propylene glycol in saline, Ct+, control group), braylin (BRA, 40 μM), RU486 (GR antagonist, 10 μM) + braylin 40 μM, dexamethasone (Dexa; 40 μM) or RU486 (10 μM) + dexamethasone (40 μM) in the presence of LPS (500 ng/mL) and IFN-γ (5 ng/mL). Cell-free supernatants were collected 4 hours after treatments for TNF-α measurement by ELISA. Ct- and RU-show concentrations of TNF-α in unstimulated cells, treated with vehicle and RU486, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SEM; n = 10 determinations per group. $Significantly different from the vehicle treated cultures unstimulated (p < 0.05); *Significantly different from the vehicle treated cultures stimulated with LPS + IFN-γ (p < 0.05). +Significantly different from the group untreated with antagonist (p < 0.05). Panel B shows the effect of braylin on the activation of NF-κB on RAW 264.7 Luc macrophages. Cells were pretreated with vehicle (50% propylene glycol in saline, Ct+, control group), braylin (BRA; 10, 20 or 40 μM) or dexamethasone (Dexa; 40 μM) for 1 hour prior to stimulated with LPS (500 ng/mL) and IFN-γ (5 ng/mL) for 3 hours. Ct- shows luciferase activity in unstimulated cells. Luciferase activity was measured in a luminometer. $Significantly different from the vehicle treated cultures unstimulated (p < 0.05); *Significantly different from the vehicle treated cultures stimulated with LPS + IFN-γ (p < 0.05). #Significantly different from the Dexa group (p < 0.05). ANOVA followed by Tukey´s multiple comparison test.