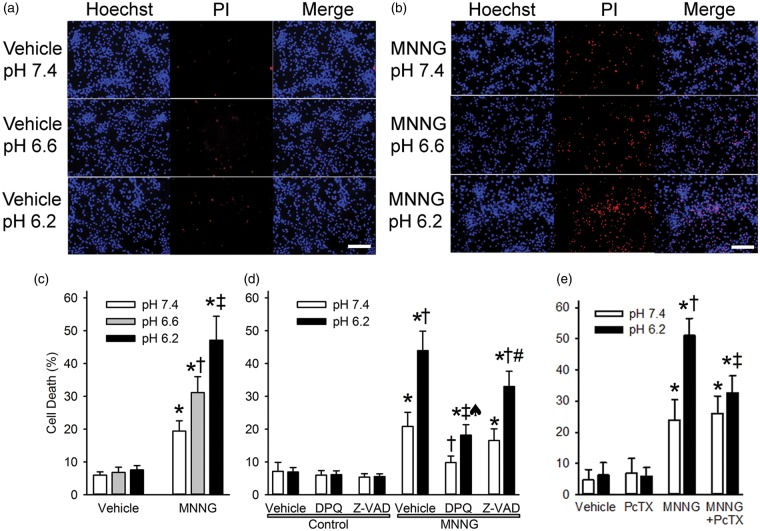
Figure 1.
Acidosis augments MNNG-induced neuronal cell death. Representative images show propidium iodide staining (PI, red) and Hoechst 33342 nuclear staining (Hoechst, blue) of cultured neurons one day after 15-min treatment with 0.1% DMSO vehicle (a) or 25 µM MNNG (b) followed by 4-h exposure to medium with a pH of 7.4, 6.6, or 6.2 (Scale bar = 200 µm). Note that the proportion of cells stained with PI progressively increased with decreasing pH after MNNG treatment. (c) Mean ± 95% confidence interval of percent cell death at 24 h after treatment with vehicle or MNNG and 4-h exposure to medium with pH 7.4, 6.6, or 6.2 (n = 10 per group). * P < 0.001 from vehicle pH 7.4 treatment; † P < 0.001 from MNNG pH 7.4 treatment; ‡ P < 0.001 from MNNG pH 7.4 and MNNG pH 6.6 treatments. (d) Percent cell death at 24 h after 15-min exposure to vehicle (0.1% DMSO; control) or MNNG followed by 4-h exposure to pH 7.4 or 6.2 medium and continuous treatment with vehicle (0.1% DMSO), the PARP inhibitor DPQ (30 µM), or the caspase inhibitor Z-VAD (100 µM). * P < 0.001 from control pH 7.4 with vehicle treatment; † P < 0.001 from MNNG pH 7.4 with vehicle treatment; ‡ P < 0.001 from MNNG pH 6.2 with vehicle treatment; ♠ P < 0.001 from MNNG pH 7.4 with DPQ treatment; # P < 0.001 from MNNG pH 7.4 with Z-VAD treatment; n = 9 per group. (e) Percent cell death at 24 h after 15-min exposure to vehicle (0.1% DMSO) or MNNG followed by 4-h exposure to pH 7.4 or 6.2 medium and continuous treatment with vehicle (0.1% DMSO) or the ASIC1a inhibitor psalmotoxin (PcTX; 0.2 µM). * P < 0.001 from vehicle pH 7.4 treatment; † P < 0.001 from MNNG pH 7.4 treatment; ‡ P < 0.001 from MNNG pH 6.2 treatment; n = 6 independent experiments per group.