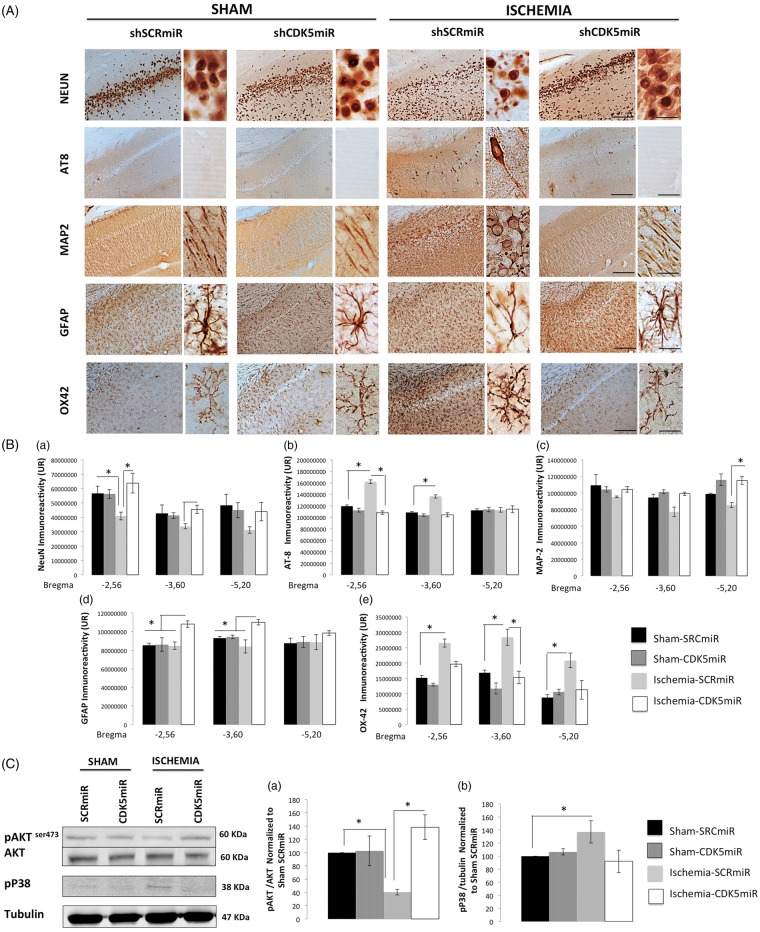
Figure 4.
CDK5 silencing reduces neurodegenerative hallmarks in CA1 at four months post-ischemia. (A) Representative immunoreactivity levels in the ipsilateral CA1 region of the hippocampus (bregma −2.56) at four months post-ischemia. The micrographs were obtained at 10 × and 40×. Scale bars=50 µm (10×) and 25 µm (40×). (B) Intensity of immunoreactivity for (a) NeuN, (b) AT-8 (c) MAP-2, (d) GFAP, and (e) OX42. These values were quantified at bregma levels of −2.56, −3.60, and −5.20. RU: relative units. *Significant differences, p ≤ 0.05; n = 4–6 animals/group. (C) Total protein levels of pAKT (Ser 473), AKT (a), and phosphorylated p38 (b) were determined by Western blotting. Densitometric quantification was determined relative to the loading control (tubulin) and normalized to the internal control (SCRmiR-treated sham rats). The values are the mean ± SEM. *Significant differences, p ≤ 0.05; n = 4–6 animals/group. CDK5, cyclin-dependent kinase 5; SCR, scrambled RNA sequence.