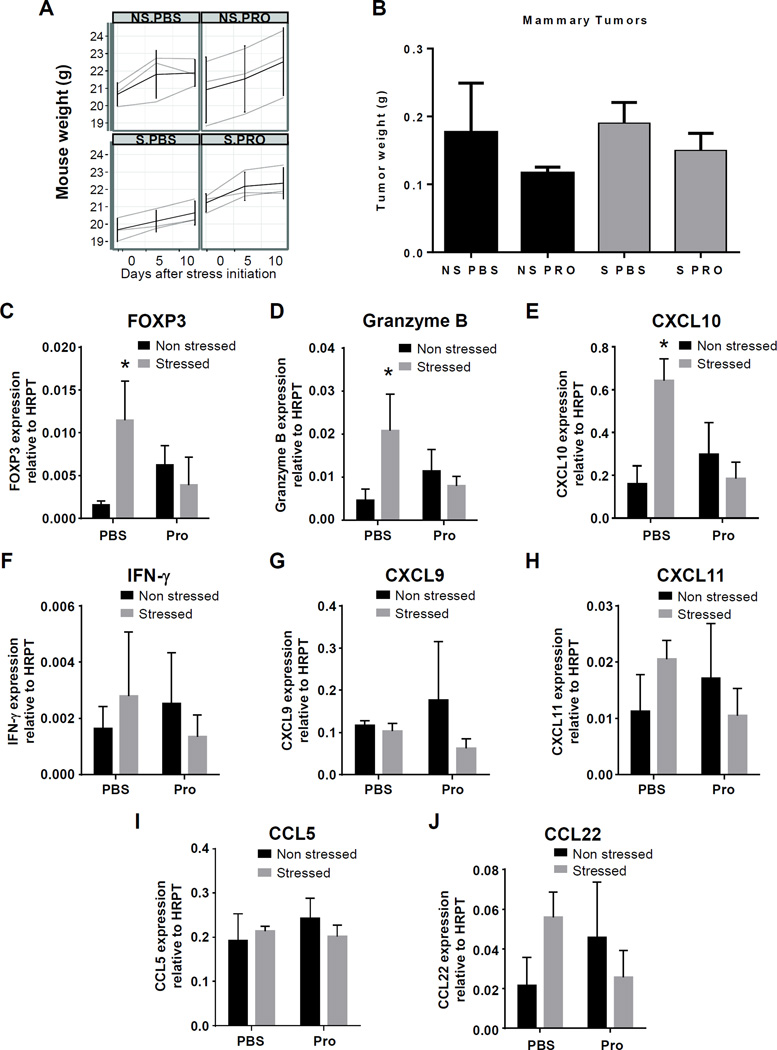
Figure 5.
Acute stress and propranolol affects immune patterns in 4T1 mammary tumor bearing mice (A) Mice with 100 mm3 mammary tumors were placed into two groups; aRRS or NS (controls). Each group was treated with either propranolol (PRO, 10 mg/kg IP every day for 3 days), or PBS as controls. Mice were weighed and monitored throughout the study. Each line represents one mouse and changes from baseline, in mouse weight, were compared to control using a repeated measures analysis of variance model. (B) Fresh tumor samples were weighed and isolated from stressed (S) and control (NS) mice; (C–J) Gene expression analyses via qRT-PCR, using tumor-extracted RNA and primers for FOXP3 (C) granzyme B (D) CXCL-10 (E) IFN-γ (F) CXCL9 (G), CXCL11 (H), CCL5 (I) and CCL22 (J). Real-time PCR data was normalized to the reference gene and differences between treatment and control were compared across stress groups using a cells means model and general linear hypothesis tests. * p < 0.05.