FIGURE 2.
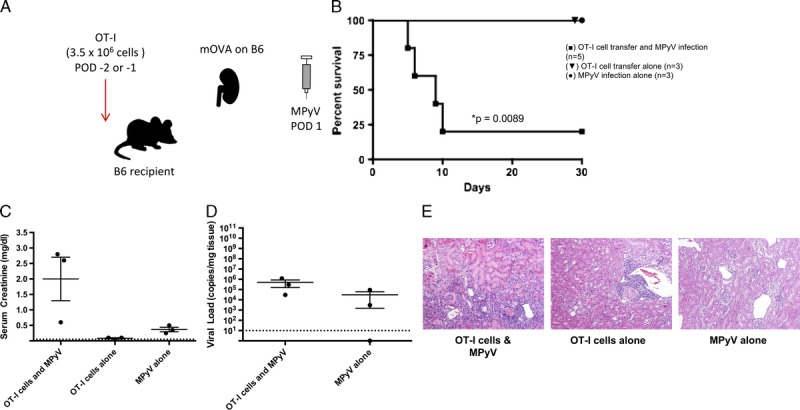
Antidonor CD8+ T cells and MPyV are both required to cause rejection. A, Experimental model for functional antidonor adoptive OT-I T cell transfer in the B6 mouse. B6 mOVA donor kidneys were transplanted into B6 recipients with bilateral nephrectomy. Mice were infected by MPyV on day 1 posttransplantation. OT-I T cells were transferred on days −2 or −1 pretransplantation. B, Survival of mice receiving MPyV infection alone (n = 3), OT-I cell transfer alone (n = 3), or both MPyV infection and OT-I cell transfer (n = 5). C, Serum creatinine at day 30 or time of death and (D) viral load in kidneys at day 30 or time of death. (The number of data points per group is decreased from initial survival curves due to mouse death before samples could be obtained). Dots represent individual mice. Dashed lines indicate limits of detection. E, Representative histology. OT-I T cell transfer and viral infection together result in a greater degree of histologic damage than either condition alone (H&E staining; original magnification, ×400).
