Figure 4. USP22 induces EMT by regulating AP4.
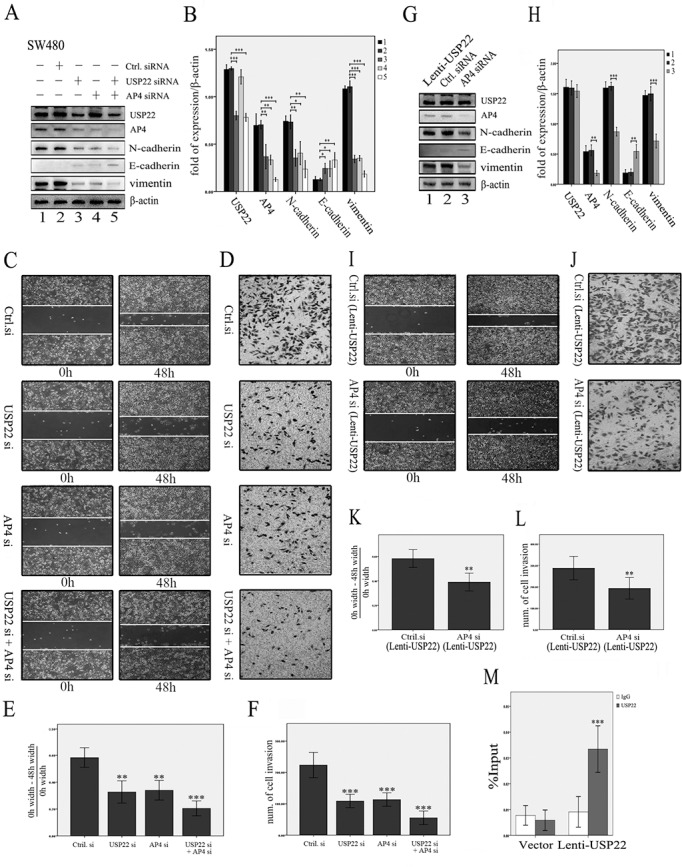
(A, B) The effects of knocking down USP22 and AP4 in SW480 cells. Western blot (WB) analysis revealed that knockdown of AP4 resulted in decreased N-cadherin, vimentin, and AP4 expression and increased E-cadherin expression, similar to the effects of USP22 down-regulation, whereas USP22 expression remained unchanged in AP4-down-regulated cells. The extent of mesenchymal-epithelial transition was greater in the double-gene (USP22 and AP4) knockdown cells than in the other cell types. (C–F). Similar results were observed in the scratch and transwell assays. (G, H) By contrast, WB analysis revealed that knockdown of AP4 reduced the expression of N-cadherin, vimentin, and AP4 and increased E-cadherin expression in lenti-USP22 cells (USP22 up-regulated cells), whereas USP22 expression remained unchanged. (I–L) Scratch and transwell assays revealed that the increased migration and invasion abilities resulting from USP22 up-regulation were significantly decreased in AP4 knockdown cells compared with the control. (M) ChIP analysis revealed that USP22 bound to the promoter region of AP4 (IgG served as a negative control). Significance level as indicated: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
