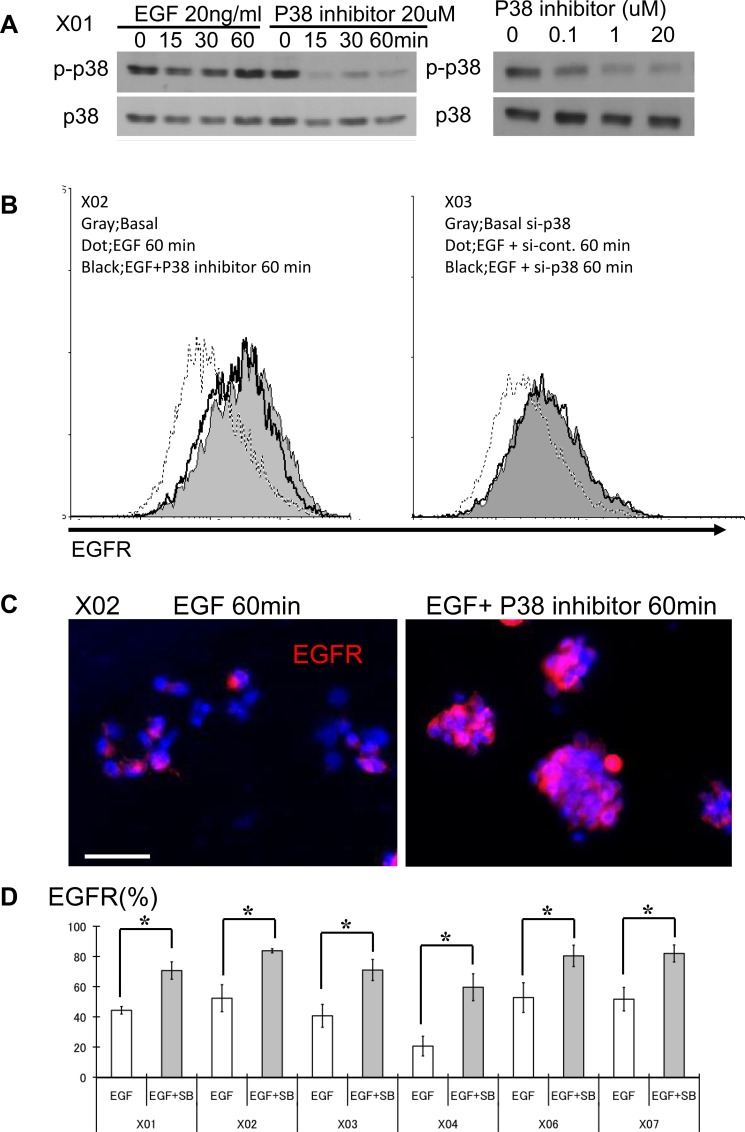
Figure 1. The p38 signaling pathway is activated in GSC and its inhibition leads to increase in surface expression of EGFR.
(A) GSC propagated with and without recombinant EGF were subjected to Western blot analysis for total and phospho-p38. GSCs were also treated with SB203580, an inhibitor of p38, at different time points and doses. (B) FACS analyses were performed with GSC at three different conditions: immediately prior to addition of EGF (20 ng/ml), 60 minutes after exposure to EGF, and 60 minutes after treatment with EGF and SB203580. FACS histograms show rapid reduction (approximately 60%) in the expression level of surface EGFR from baseline (solid gray) to addition of EGF (dotted line). This reduction is abrogated in the presence of the p38 inhibitor (10 μM SB203580) (black line). (C) Immunocytochemical staining was performed with an antibody directed against the extracellular domain of the EGFR. GSC exposed to the p38 inhibitor (10 μM SB203580) show higher surface expression. Bar = 50 μm. (D) Six distinct GSC lines were propagated in the presence of EGF (20 ng/ml), with and without the p38 inhibitor (10 μM) and the surface expression level of EGFR was determined by FACS analysis. All GSC lines revealed increase in EGFR expression in the presence of p38 inhibitor. The results shown in the graph are mean + S.D. from three experiments. *p < 0.05.