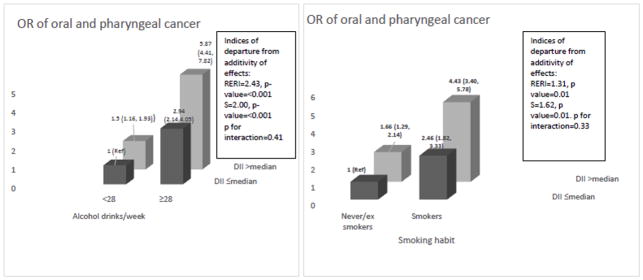
Fig. 1.
Odds ratios (OR)a and 95 % confidence intervals for oral and pharyngeal cancer according to the combination of of dietary inflammatory index (E-DII) and alcohol and smoking. Italy, 1992–2009.
Footnote:
Abbreviation: RERI: Relative excess risk due to interaction; S: Synergy index.
aEstimated from multiple logistic regression models, including terms for age, sex, centre, education, body mass index, non-alcohol energy intake, and tobacco smoking and alcohol consumption when appropriate.