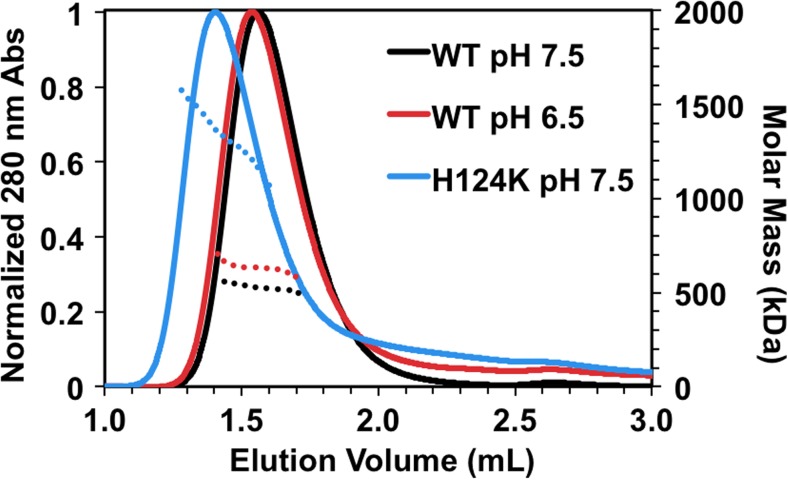
Fig. 2.
The H124K mutation induces formation of expanded oligomers but also increases the proportion of smaller oligomers. One-hundred micromolar samples were incubated at 37 °C prior to injection onto a Superose 6 SEC column and analyzed by multi-angle light scattering (MALS). Calculated molar mass is shown (dotted lines) for the top 50% of the UV chromatogram for each sample. WT-HSPB1 elutes at a slightly earlier volume at pH 6.5 relative to pH 7.5 and has a larger average molar mass, corresponding to an increase in the number of subunits. At pH 7.5, H124K-HSPB1 elutes earlier than WT with a substantial increase in molar mass (see Table 1). The elution profiles of both WT-HSPB1 at pH 6.5 and H124K-HSPB1 at pH 7.5 have long tails at longer elution times, indicting an increase in the proportion of small oligomers. These data together suggest that destabilization of the dimer interface destabilizes the oligomers while paradoxically expanding their size