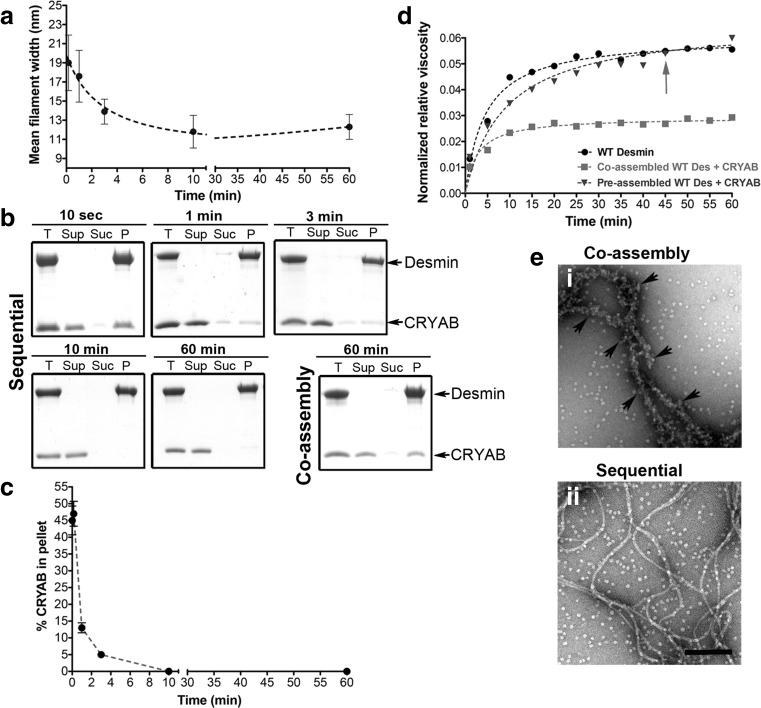
Fig. 4.
CRYAB binds to desmin assembly intermediates. a Graph of the change in desmin filament widths at different time points after the initiation of assembly. b CRYAB was added sequentially (sequential) to desmin oligomers at the indicated time points and their interaction analysed by co-sedimentation assay. For comparison, CRYAB was also coassembled with desmin (coassembly). c CRYAB binding to desmin sharply decreases as the filaments assemble via the sequential assembly regime, yielding undetectable CRYAB binding after 10 min. The mean values (mean ± SD) of three independent assays are shown. All samples were assembled for a total duration of 120 min. Abbreviations for collected fractions: T total, Sup supernatant, Suc sucrose, P pellet. d Viscometry measurements were obtained for WT desmin alone (circle), desmin coassembled with CRYAB (square) and the addition of CRYAB after 45 min (arrow) to a desmin assembly mix (triangle). Coassembly of CRYAB with desmin reduced the sample viscosity by 50% as compared to WT desmin or the preassembled desmin. e Electron micrographs compare desmin coassembled with CRYAB after 120 min (i) to CRYAB added after 60 min to preassembled desmin and incubated for a further hour (ii). Note that with CRYAB coassembly, the filament backbone of desmin is almost totally covered by CRYAB particles. Scale bar = 100 nm