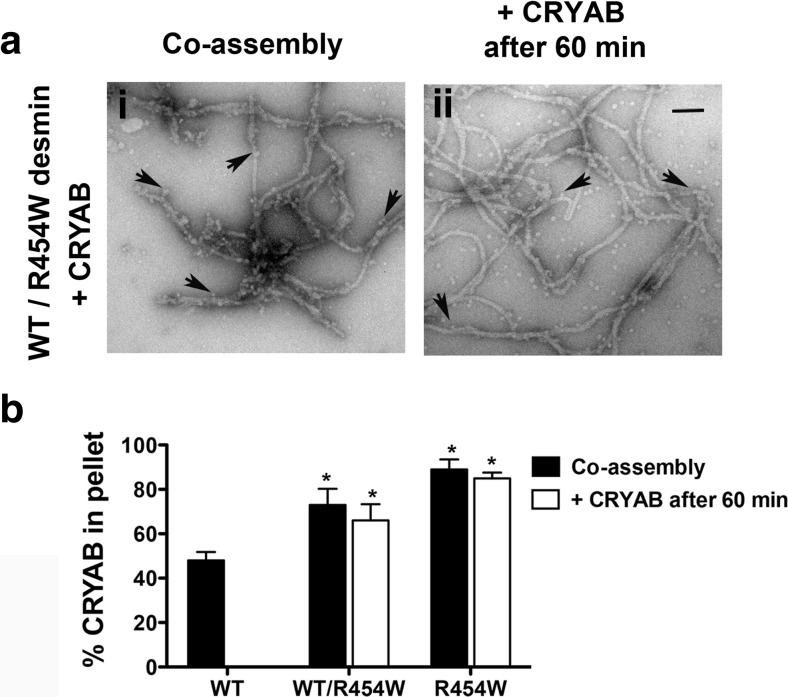
Fig. 7.
Alterations in the filament topology of mutant desmin R454W promote excessive CRYAB binding. a Electron micrographs compare the CRYAB bound to desmin filaments using equimolar mixtures of WT and R454W desmin in either coassembly (a i) or addition of CRYAB 60 min after assembly was started (a ii). Samples were fixed in 0.1% (v/v) glutaraldehyde after assembly prior to EM. Bound CRYAB particles are indicated (arrows). Scale bar 100 nm. b Bar graph shows the quantification of pelletable CRYAB obtained after coassembly with the different desmin preparations. When coassembled, WT desmin exhibited decreased binding to CRYAB as compared to heterozygous or homozygous mutant desmin R454W (black bars). No binding to WT desmin was detected when CRYAB was added after filament maturation. In contrast, both heterozygous and homozygous desmin R454W show enhanced CRYAB binding (white bars). The mean ± SD of three independent experiments is shown