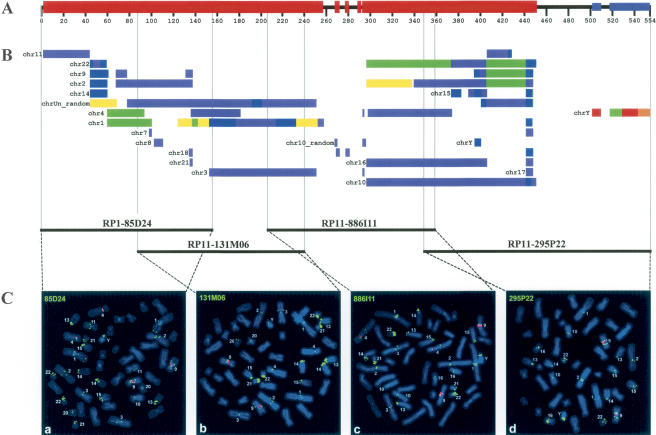
Figure 3.
Summary scheme depicting homologies between the pericentromeric region of Yq11 and other chromosomes. (A) The black horizontal bar shows the 554-kb sequenced region. Segments with interchromosomal (red boxes) and intrachromosomal (blue boxes) duplications are indicated. (B) All colored bars represent sequence homologies between the Y-chromosomal pericentromeric region and autosomes as determined by standard whole-genome analysis comparison (WGAC). Each color indicates a specific degree of homology: red, 100%-99%; orange, 99%-98%; yellow, 98%-97%; green, 97%-96%; blue, 96%-95%; indigo, 95%-94%; and violet, 93%. Each bar is preceded by the corresponding chromosome number. Bars that correspond to different chromosomes are indicated separately. Paralogies to sequenced genomic regions not assigned to a specific chromosome are summarized as chrUn_random. (C) Two-color FISH of human Y-chromosomal PAC (85D24) and BAC (131M06, 886I11, 295P22) clones (labeled in green) to human male metaphase spreads is shown below. Centromeres of chromosomes 4 and the constitutive heterochromatic region of the long arm of chromosomes 9 are labeled in red. Metaphases shown in a-d reflect the most proximal (a) to distal (d) order in the contig. Chromosomes with specific hybridization signals are tagged, respectively. The in silico identified paralogous segments and the chromosomal band localizations of the specific signals are listed in Table 1.