Figure 5.
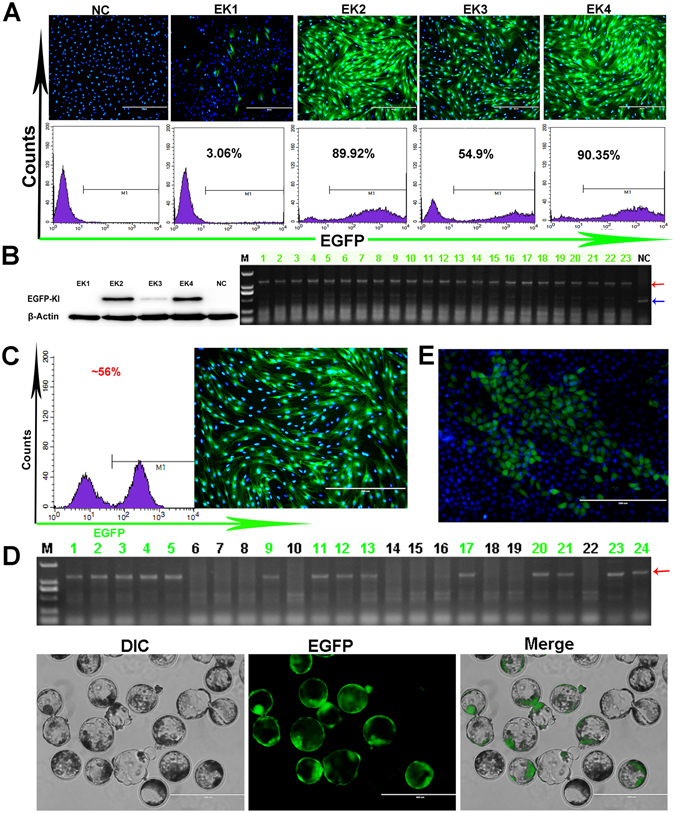
Application of the EGFP-KI reporter PFFs. (A) The purity of each EGFP gene site-specific knock-in cell clones was analysed via fluorescence microscopy and confirmed via FACS. (B) To confirm of the purity of each cell clone by western blotting (shown on the left); Genomic PCR analysis of the blastocysts (shown on the right); these 23 nuclear donor cells were derived from cell clone-EK4. The results show the high purity of cell clone-EK4. The red arrow indicates the knock-in bands and the blue arrow indicates the wild-type bands. NC: negative control. (C) The proportion of mixed nuclear donor cells was analysed via fluorescence microscopy and confirmed via FACS. (D) Genomic PCR analysis of the blastocysts (upper). Nuclear donor cells were derived from the mixed nuclear donor cells in fig. C . The red arrow indicates the knock-in bands. After 7 days of culture, the mixed blastocysts were observed by fluorescence microscopy (lower). M: D2000. (E) Generation of the EGFP reporter PK-15 cell lines was confirmed via fluorescence microscopy.
