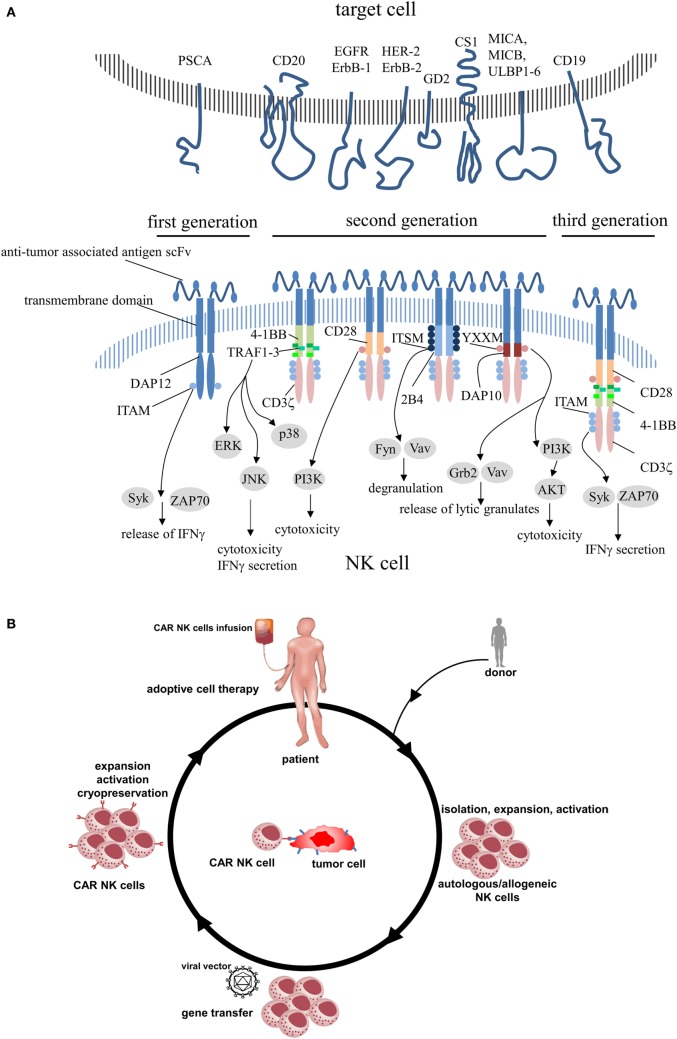
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic structures of various chimeric antigen receptors applied in engineered primary human NK cells including its intracellular signaling domains. (B) CAR NK cell therapy. Autologous NK cells or donor NK cells (allogeneic) are isolated, expanded, and activated by cytokines. After modification of NK cells to express CAR, NK cells are expanded, activated, and administered to the patient or frozen for long-term preservation. PSCA, prostate stem cell antigen; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; HER-2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; GD2, disialoganglioside 2; CS1, CD2 subset 1; MICA/B, MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence A/B; ULBP1-6, UL16-binding proteins 1–6; DAP, DNAX-activation protein; ITAM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif; Syk, spleen-associated tyrosine kinase; ZAP70, zeta-chain-associated protein kinase 70; TRAF, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; I3K, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase; ITSM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif; Fyn, Src family tyrosine kinase; Vav, vav guanine nucleotide exchange factor; YXXM, phosphorylation motif; Grb2, growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; AKT, protein kinase B.