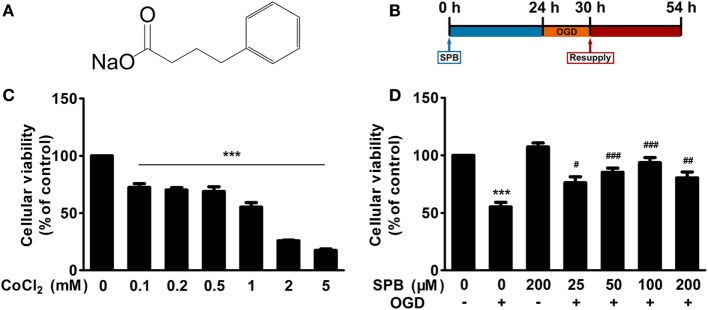
Figure 1.
Sodium phenylbutyrate (SPB) improves cellular viability from ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in a CoCl2-induced oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD) cell model in SH-SY5Y cells. (A) Chemical structure of SPB. (B) Experimental protocol of SPB treatment and cellular I/R model. SH-SY5Y cells were treated with SPB for 24 h and then were administered OGD by CoCl2 along with no-glucose culture medium for 6 h, followed by culturing in 10% FBS with DMEM for 24 h in a normal cell incubator to mimic reperfusion. This protocol was used in all cellular experiments unless otherwise indicated. (C) Effect of different concentrations of CoCl2 on the cellular viability of SH-SY5Y cells as assessed by the MTT assay. The procedure of this experiment was described above, except for no SPB treatment before OGD and different concentrations of CoCl2. ***p < 0.001, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), n = 4. (D) The protective effect of graded concentrations of SPB on CoCl2-induced I/R injury. CoCl2 (1 mM) was used to perform OGD. Cellular viability was measured by the MTT assy. ***p < 0.001, vs. the control group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, vs. OGD without the SPB group, one-way ANOVA, n = 4.