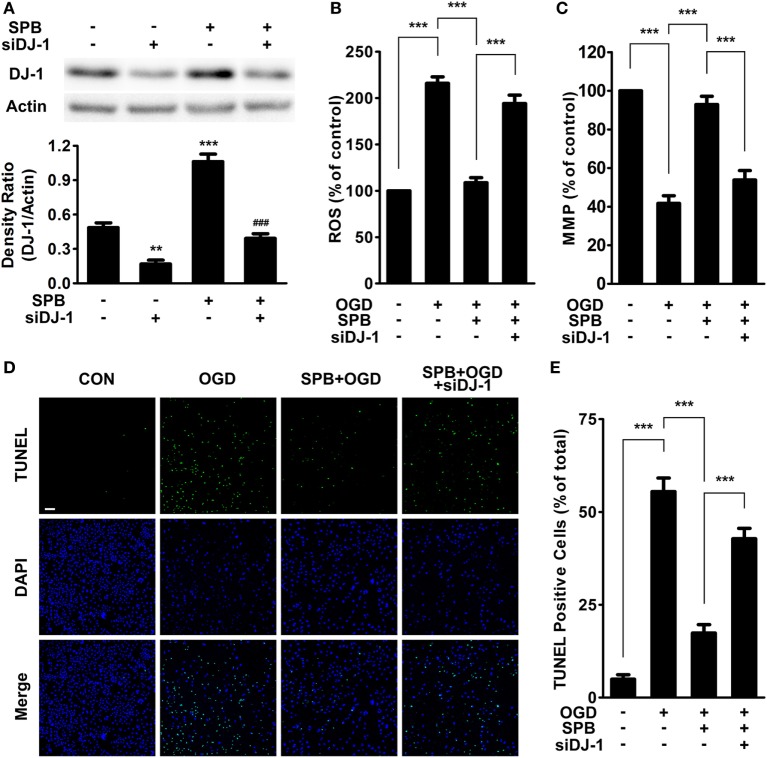
Figure 3.
Sodium phenylbutyrate (SPB) ameliorates mitochondrial impairment and cellular apoptosis induced by oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD) via DJ-1 signaling in SH-SY5Y cells. (A) SH-SY5Y cells were treated with or without SPB and then were transfected with siRNA targeting human DJ-1 for 48 h, followed by western blot analysis to confirm the effective knockdown of the DJ-1 protein level. The graph below indicates the quantification of the DJ-1 level, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. the control group; ###p < 0.001 vs. the SPB-treated group; one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), n = 3. Measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (B) and the mitochondrial membrane potential (C) in SH-SY5Y cells. Cells were pretreated with SPB for 24 h and were transfected with DJ-1 siRNA or control siRNA for 24 h, followed by OGD treatment as described in Figure 1B. ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA, n = 3. TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining (D) and quantitative analysis (E). The bar represents 200 µm (green: TUNEL; blue: DAPI). The treatments were the same as those described above. ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA, n = 4.