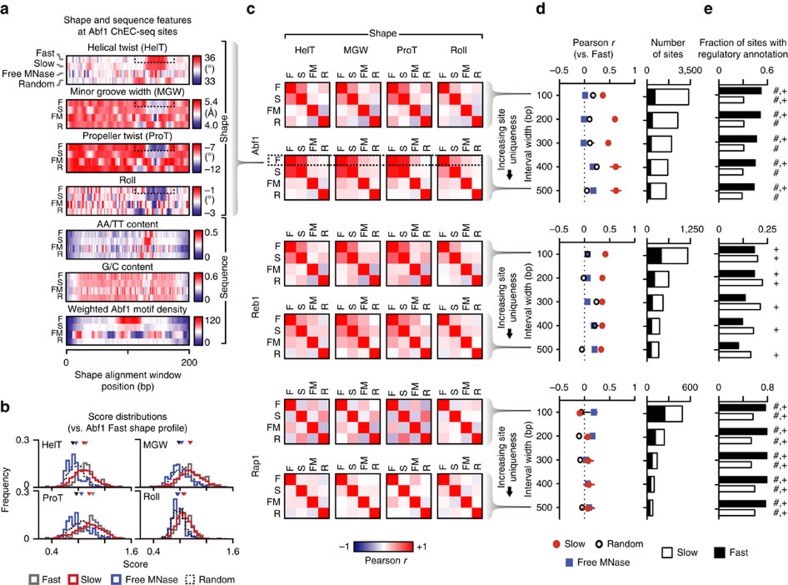
Figure 1. Slow ChEC-seq sites have characteristic shapes separate from TF-binding motifs.
(a) Average shape and sequence features for unique fast (F) and slow (S) Abf1 sites 500 bp from other ChEC sites compared to free MNase (FM) and random (R) control sites aligned using shape features. Motif density was computed by weighting occurrences based on motif score. (b) Distributions of scores from searching shape vectors using the Abf1 fast site shape profile for fast and slow Abf1 sites (500 bp from other ChEC sites) and free MNase and random control sites; triangles represent the median score for each distribution. The shape profile used for searching is indicated in the dotted boxes in a. (c) Pearson correlations of average DNA helix twist (HelT), minor groove width (MGW), propeller twist (ProT), and roll features for unique fast and slow Abf1, Reb1 and Rap1 sites 100 bp (top) or 500 bp (bottom) from other ChEC sites compared to control sites aligned using shape features. (d) Pearson correlations compared to fast sites of aligned average DNA shape features at a variety of interval widths and the number of sites at each interval width. Error bars represent mean±s.e.m. (e) Proportion of unique sites at a range of overlap interval widths with known or proposed regulatory associations. P values<0.1 under Fisher's exact test versus FM and R control sites are indicated with ‘#' and ‘+', respectively.