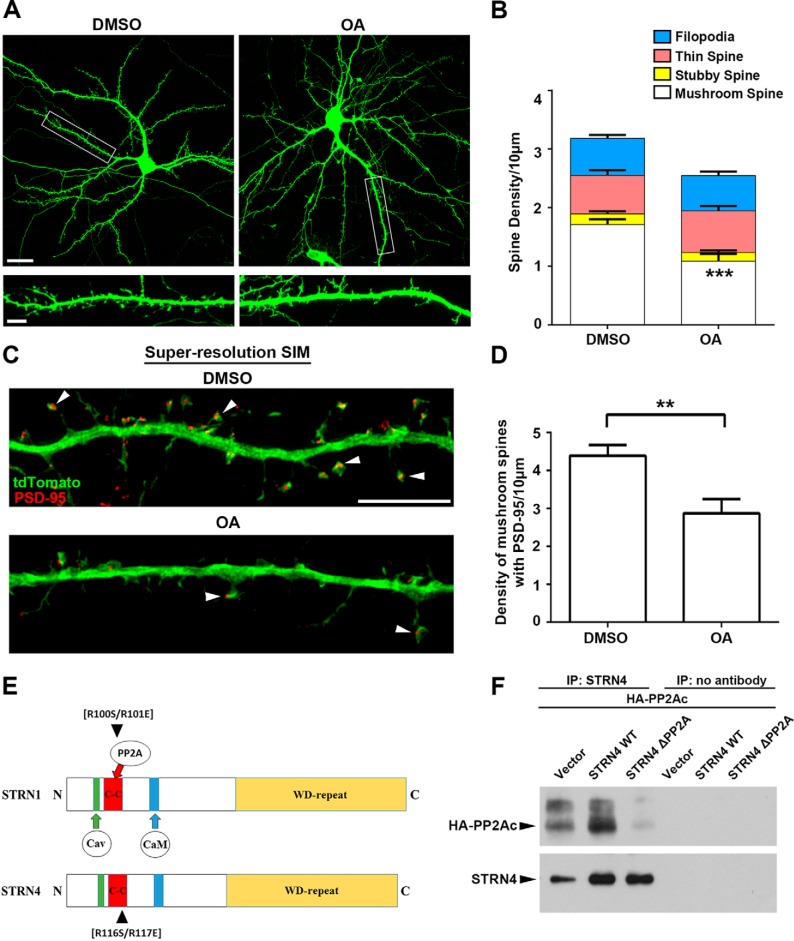
Figure 6.
PP2A inhibition affects spine morphology. A, hippocampal neurons (13 DIV) were transfected with GFP. Cells were treated with DMSO (vehicle control) or okadaic acid (OA, 30 nm) for 4 h at 18 DIV before fixation and immunostained with GFP antibody. Representative images taken by confocal microscopy are shown. Scale bars, 20 μm (upper) or 5 μm (lower). B, inhibition of PP2A by okadaic acid significantly reduced the density of mushroom spines, but not the stubby spines, thin spines, and filopodia. (15 dendrites from 9 neurons in each group were quantified.) C, hippocampal neurons (13 DIV) were transfected with tdTomato and PSD-95 intrabody and treated with DMSO (vehicle control) or okadaic acid (30 nm) for 4 h at 18 DIV before fixation. Neurons were immunostained by RFP and GFP antibodies to visualize the tdTomato and PSD-95, respectively. Representative images acquired by SR-SIM showing mushroom spines that contained PSD-95 clusters in the spine heads (arrowheads). D, okadaic acid treatment significantly reduced the density of PSD-95-positive mushroom spines. Results were pooled from two independent experiments (21–22 dendrites from 16 to 19 neurons for each group were quantified). Scale bar, 5 μm. E, schematic diagram illustrating the conserved domains between STRN1 and STRN4, and the position of the two arginine residues that are important for binding to PP2A. F, plasmid construct of HA-tagged PP2A catalytic subunit α isoform (PP2AC) was co-transfected with wild-type STRN4 or STRN4-R116S/R117E double mutant (ΔPP2A) into HEK-293T cells. Much less STRN4-ΔPP2A was co-immunoprecipitated with PP2AC compared with the wild-type STRN4. Data are mean ± S.E.; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001, Student's t test.