Figure 1.
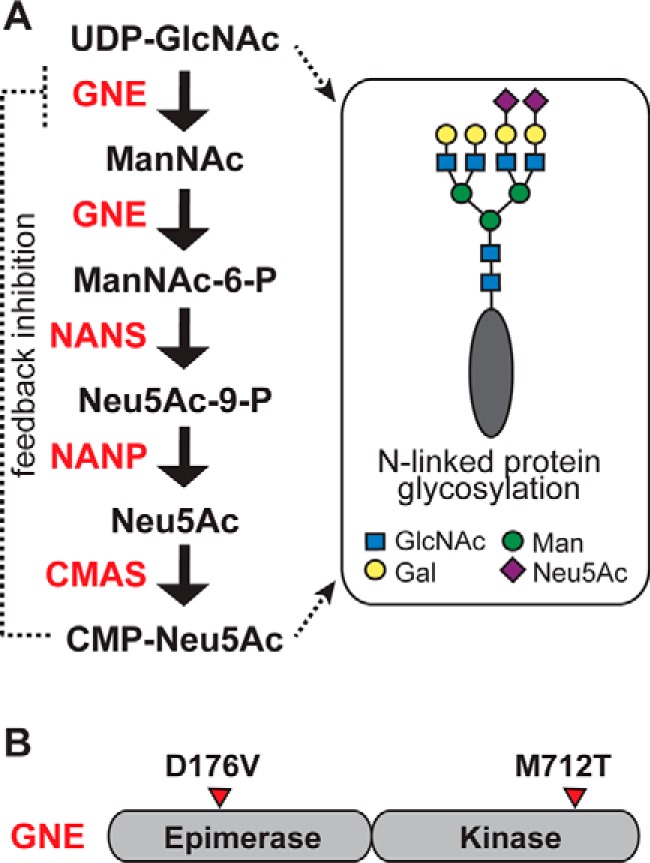
GNE is a key regulator of sialic acid production. A, GNE catalyzes two steps in sialic acid production: epimerization of UDP-GlcNAc, producing ManNAc, and phosphorylation of ManNAc, producing ManNAc-6-P. Subsequent steps convert ManNAc-6-P to Neu5Ac and then to CMP-Neu5Ac. Both UDP-GlcNAc and CMP-Neu5Ac are precursors to N-linked glycan biosynthesis. CMP-Neu5Ac inhibits the activity of GNE through a feedback mechanism. B, GNE is a bifunctional enzyme with an N-terminal epimerase domain and a C-terminal kinase domain. Mutations associated with GNE myopathy are found in both domains. The D176V and M712T mutations are examined here.
