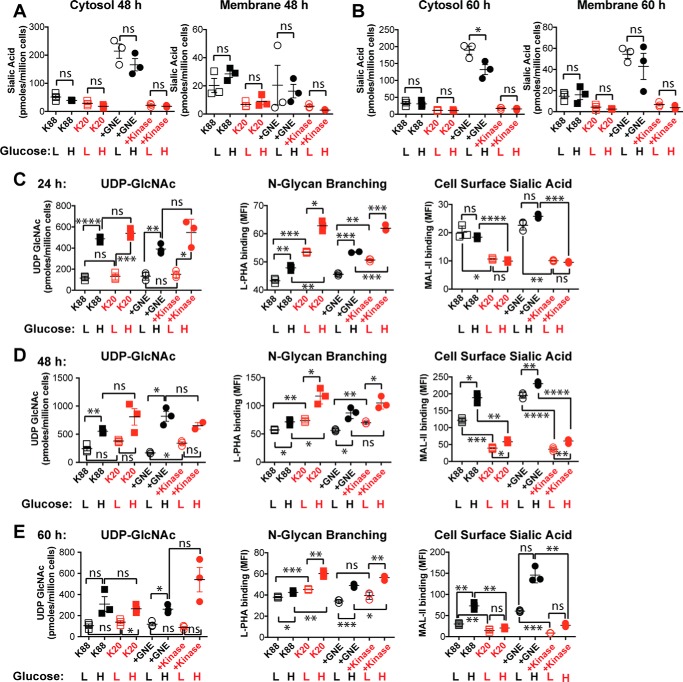
Figure 5.
Reduced glucose supplementation led to reduced UDP-GlcNAc levels and reduced N-linked glycan branching. Cell lines were cultured with 0.5 g/liter glucose (low (L)) or 2 g/liter glucose (high (H)). Cytosolic and membrane-associated sialic acid were quantified by DMB derivatization with detection by fluorescent HPLC after cell culture in high and low glucose media for 48 h (A) and 60 h (B). In addition, UDP-GlcNAc levels were quantified by HPAEC with UV detection, and cell surface L-PHA and MAL-II lectin binding were measured by flow cytometry after culturing cells for 24 h (C), 48 h (D), or 60 h (E). Cell lines labeled in black produced sialic acid, whereas cell lines labeled in red did not express an active GNE epimerase domain and consequently could not synthesize sialic acid. For all panels, data shown represent three biological replicates, with error bars depicting the mean and S.E. For flow cytometry experiments, each data point represents the MFI of a single sample, typically of 10,000 cells. Flow cytometry experiments were performed at least twice. Statistical significance determined by unpaired Welch's test: **** indicates a p value < 0.0001, *** indicates a p value < 0.001, ** indicates a p value < 0.01, and * indicates a p value < 0.05. ns indicates difference not statistically significant.