Figure 1.
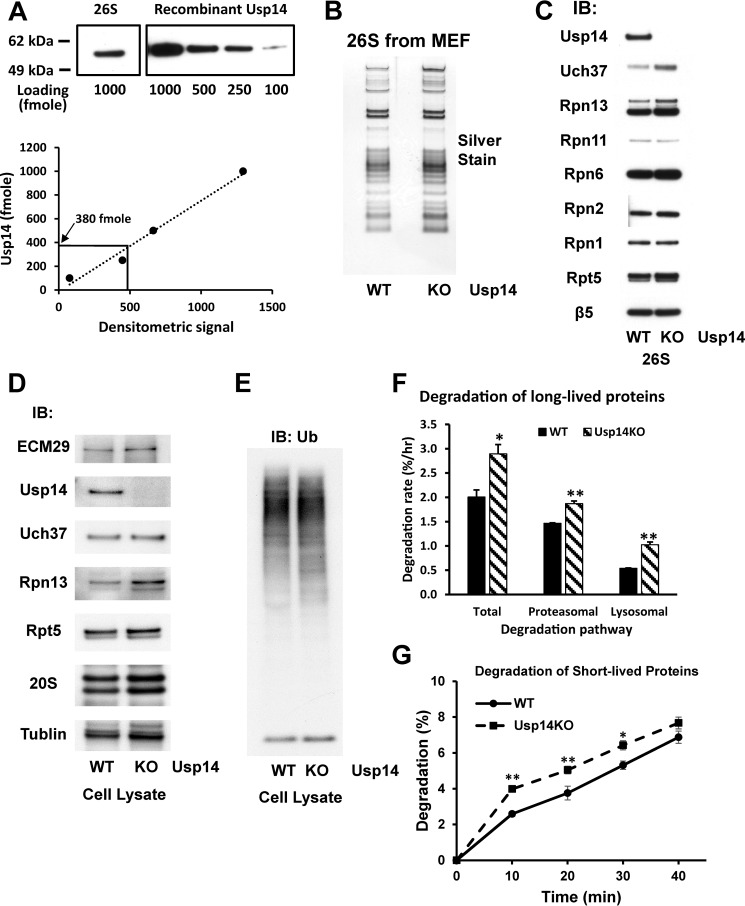
MEF cells lacking Usp14 have increased content of Rpn13 and Uch37 in the 26S proteasomes. Proteasomes were purified from WT and Usp14KO MEFs using the UBL method (see “Experimental procedures”). Concentrations of each proteasome preparation were determined using the BCA method, and molarities were calculated using 2.5 MDa as the molecular mass of 26S proteasomes. A, Usp14 is a substoichiometric component of WT MEF 26S. The content of Usp14 in 1 pmol of WT 26S proteasomes was determined by Western blotting using recombinant Usp14 as the standard. The content of Usp14 in 1 pmol of WT MEF 26S was calculated as 380 fmol. Upper panel, Western blot. Lower panel, quantitation from upper panel using ImageJ software. B, SDS-PAGE of purified 26S proteasomes from WT and Usp14KO MEFs. Proteins were silver-stained after electrophoresis. C, the contents of Uch37 and Rpn13 were increased in the purified 26S proteasomes from Usp14KO MEFs even though Usp14KO 26S contains the same levels of other subunits as WT 26S. Levels of proteins in 26S proteasomes purified from WT and Usp14KO MEF were determined by Western blotting after SDS-PAGE. D, the expression of Rpn13 was increased in Usp14KO MEFs. Levels of proteasome subunits were determined by Western blotting of cell lysates of WT and Usp14KO MEFs after SDS-PAGE. Unlike the purified proteasomes, only the content of Rpn13, but not that of Uch37, was increased in Usp14KO MEF cells. Therefore, this increase in Uch37 content must be due to increased binding of Rpn13. The content of tubulin was monitored as an input control. E, the cellular content of Ub conjugates did not change significantly in Usp14KO MEFs. The levels of Ub conjugates were determined in lysates of WT and Usp14KO MEFs by Western blotting after SDS-PAGE. F, MEF cells lacking Usp14 degrade long-lived cell proteins faster than WT MEFs. WT and Usp14KO MEF cells were labeled with [3H]phenylalanine (5 μCi/ml) for 24 h. After washing the cells with PBS and then chase medium (DMEM containing 2 mg/ml nonradioactive phenylalanine and 100 μm cycloheximide), cells were grown for a further 2 h to let short-lived labeled proteins be degraded. Then cells were grown in the chase medium with either DMSO (control) or 10 μm bortezomib/Velcade dissolved in DMSO to block proteasome activity. After 1 h of inhibitor treatment, degradation of cellular proteins was measured in the chase medium for up to 4 h. Proteasomal degradation rates were calculated by subtracting the degradation rate with bortezomib treatment from the total degradation rate. Error bars represent S.D. The remaining proteasome-independent proteolysis represents lysosomal proteolysis. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 compared with WT MEF by Student's t test. G, MEF cells lacking Usp14 degrade short-lived cell proteins faster than WT MEFs. WT and Usp14KO MEF cells were labeled with [3H]phenylalanine (10 μCi/ml) for 20 min. After washing the cells as in F, cells were incubated for 10 min in the chase medium. Degradation of cellular proteins was then measured in the chase medium for up to 40 min. Error bars represent S.D. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 compared with WT MEF by Student's t test. n = 6. IB, immunoblotting.