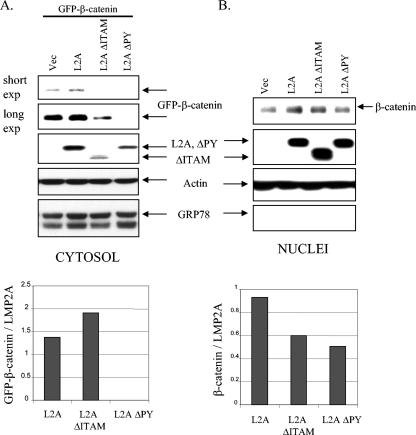
FIG. 3.
The ITAM and PY motifs contribute to the effects of LMP2A on β-catenin stabilization and nuclear translocation. HFK cells were cotransfected with GFP-β-catenin in combination with pSG5, pSG5-LMP2A, pSG5-LMP2A ΔITAM, or pSG5-LMP2A ΔPY. Supplements were withheld for 24 h prior to harvesting. Upon harvesting, cells were fractionated into their cytosolic (A) and nuclear (B) compartments and analyzed by immunoblotting. (A, top) Anti-GFP immunoblotting determined levels of GFP-β-catenin in the cytosols of transfected cells, and anti-HA detected expression of the LMP2A constructs. Antiactin and anti-GRP78 blot assays were included to assess protein loading and the integrity of the fractionation procedure, respectively. (A, bottom) Densitometry was performed, and GFP-β-catenin levels were normalized to the expression of LMP2A and graphed. (B, top) Nuclear β-catenin was detected with antibodies against β-catenin, and LMP2A expression was determined with anti-HA antibodies. GRP78 is an endoplasmic reticulum marker, and anti-GRP78 immunoblotting indicated the purity of the nuclear extracts. An antiactin immunoblot served as a protein loading control. (B, bottom) Densitometry was performed, and β-catenin levels were normalized to the expression of LMP2A and graphed. Vec, vector; exp, exposure.