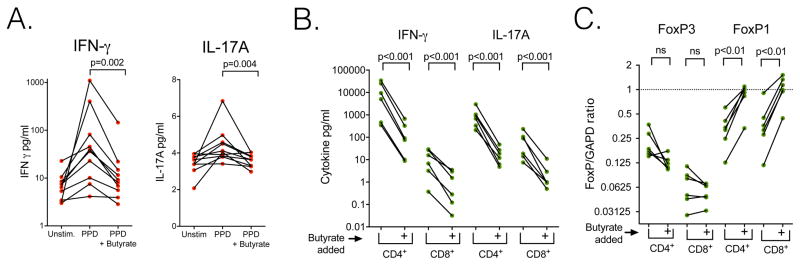
Figure 2. Butyrate inhibits IFN-γ and IL-17A production after M. tuberculosis antigen stimulation and induces FoxP1 mRNA in CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes.
A. Compared with PPD, butyrate inhibits IFN-γ and IL-17A production by PPD stimulation. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells of HIV-infected individuals on ART with latent tuberculosis were cultured in vitro without stimulation for three days (Unstim.), with PPD for three days (PPD) or with 2mM butyrate added with PPD three days (PPD+ Butyrate). Paired t test of log transformed data. B. Addition of 2mM butyrate inhibits IFN-γ and IL-17A expression in CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28. Lymphocytes from 6 different individuals are shown. Paired t test of log transformed data. C. Addition of 2mM butyrate increases FoxP1 mRNA expression in CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes. Paired t test of log transformed FoxP/GAPDH.