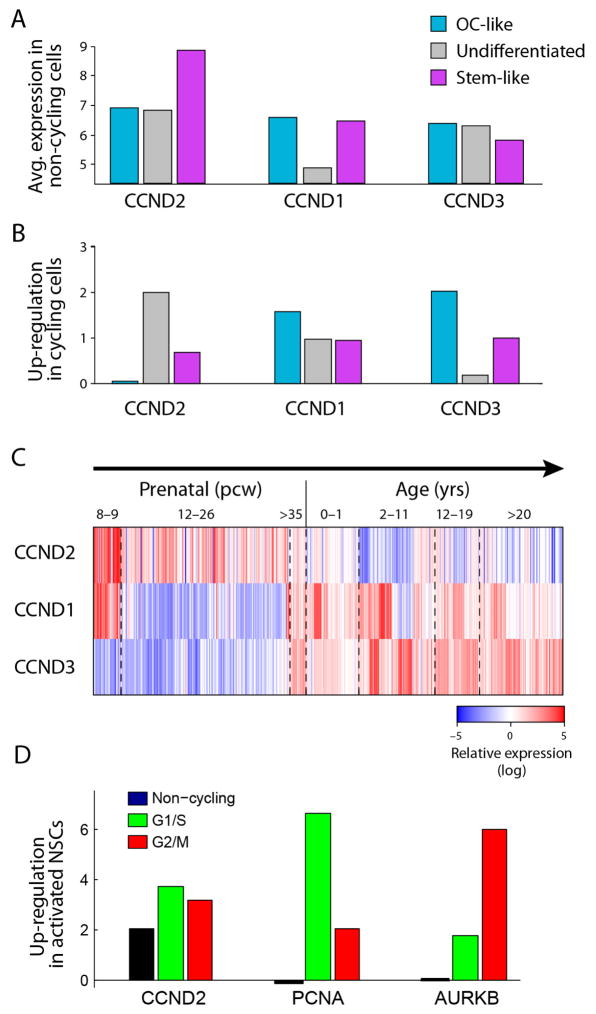
Extended Data Figure 7. CCND2 is associated with both cycling and non-cycling stem/progenitor cells.
a, CCND2, but not CCND1 or CCND3, is upregulated in non-cycling stem-like oligodendroglioma cells. Shown are the average expression levels (y axis, log-scale) of three cyclin D genes (x axis) in non-cycling cells classified as OC-like cells (light blue), undifferentiated cells (grey) and stem-like cells (purple). CCND2 is approximately fourfold higher in stem-like non-cycling cells than in OC-like and undifferentiated cells (P < 0.001 by permutation test). Conversely, CCND1 and CCND3 are expressed at comparable levels in stem-like and OC-like cells. b, Upregulation of cyclin D genes in cycling cells compared to non-cycling cells. As in a but for up regulation (log2-ratio) in cycling cells vs. non-cycling cells. CCND2 levels further increase in cycling undifferentiated and stem-like cells but not in OC-like cells, whereas CCND1 and CCND3 levels increase in OC-like cycling cells more than in undifferentiated and stem-like cycling cells. c, Distinct expression patterns of cyclin D genes in human brain development. Shown are the expression patterns of three cyclin D genes (rows) in human brain samples at different points in pre- and post-natal development, sorted by age (columns) from the Allen Brain Atlas15. CCND2 is associated with prenatal samples, whereas CCND1 and CCND3 are expressed mostly in childhood and adult samples. d, CCND2 is upregulated in activated versus quiescent NSCs19, both among cycling and non-cycling cells. Activated NSCs were partitioned into non-cycling cells (black) and cycling cells in the G1/S (green) or G2/M (red) phases (Methods). Expression difference (y axis) for each of three genes (x axis) was quantified for each of these subsets as the log2-ratio of the average expression in the respective subset versus the quiescent NSCs, and was significant for each of the three subsets (P < 0.05 by permutation test). Although CCND2 (left) is induced in both cycling and non-cycling activated NSCs, two canonical cell cycle genes (PCNA, middle; and AURKB, right) are not induced in non-cycling genes but were induced preferentially in G1/S and G2/M cells, respectively.