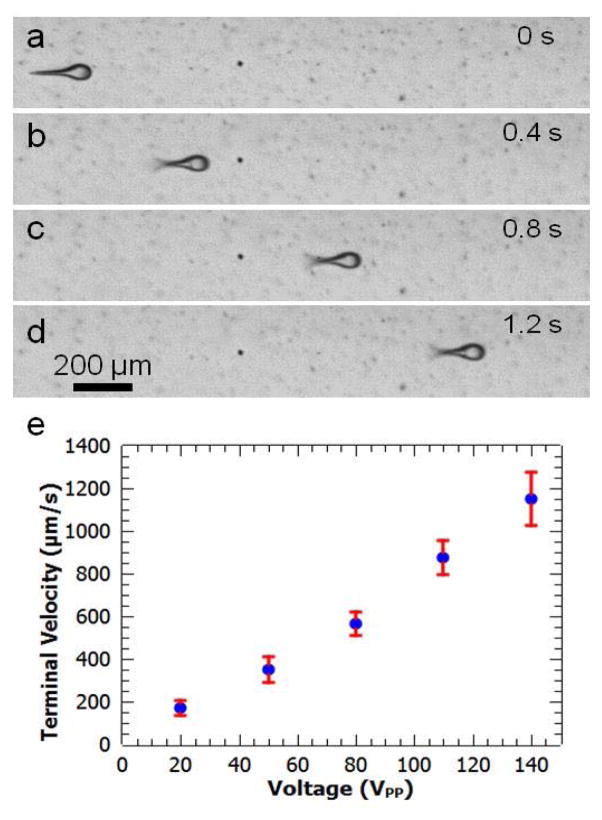
Fig. 4.
Characterization of microswimmers’ directional movement. (a) Microswimmer is stationary in the absence of acoustic oscillation. (b) Actuating the PZT transducer at 140 VPP, the microswimmer’s flagella oscillates and it moves directionally. (c) and (d): Under constant excitation voltage (140 VPP), the microswimmer moves at a constant velocity. (e) The terminal velocity of a microswimmer as a function of voltage, increasing from 220 μm/s at 20 VPP to 1200 μm/s at 140 VPP.