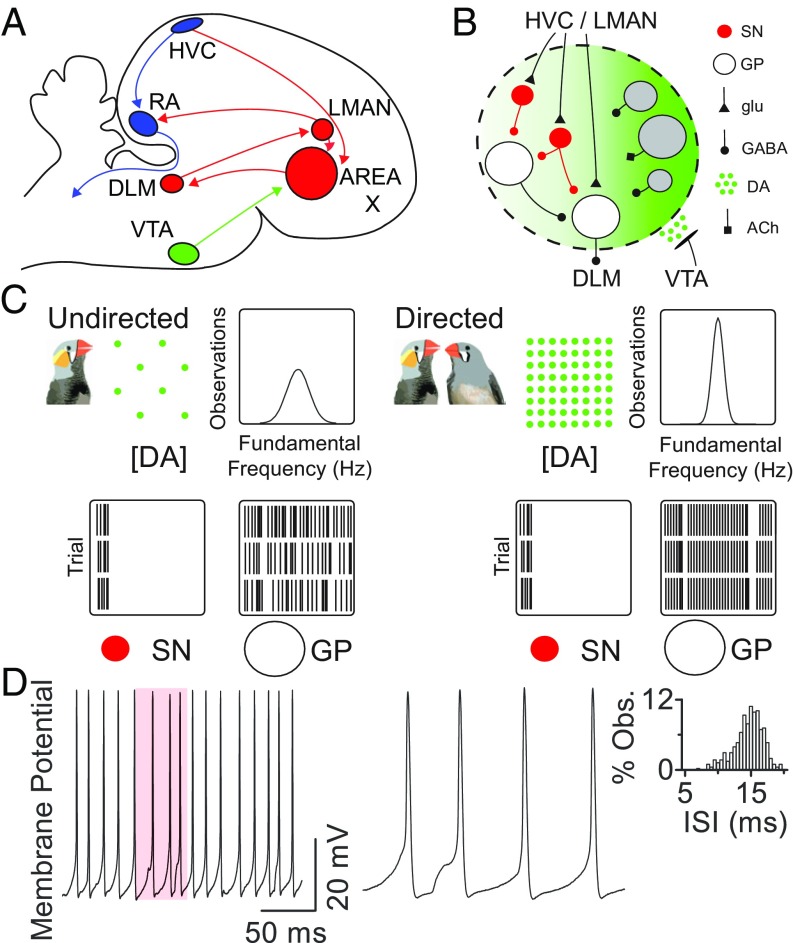
Fig. 1.
Effects of social context and dopamine on area X neuron firing. (A) Diagram of the songbird brain. Blue, motor pathway; red, learning pathway; green, midbrain dopamine input. (B) Circuitry within area X. Red, spiny neurons (SN); gray; local interneurons; white, pallidal neurons (GP). ACh, acetylcholine; DA, dopamine; glu, glutamate. (C) Schematic of social context-dependent changes in behavior and neural activity in area X (after refs. 20 and 23). During courtship, area X DA rises, narrowing the distribution of fundamental frequency across song trials. Simultaneously, area X GP output neuron firing becomes less variable. Input SNs maintain precise firing. (D) Regular pallidal neuron firing. (Left) Example pallidal neuron recording in current-clamp configuration with no current injection. (Center) Magnification of shaded region at Left illustrates underlying synaptic potentials. (Right) Interspike interval (ISI) distribution for this neuron.