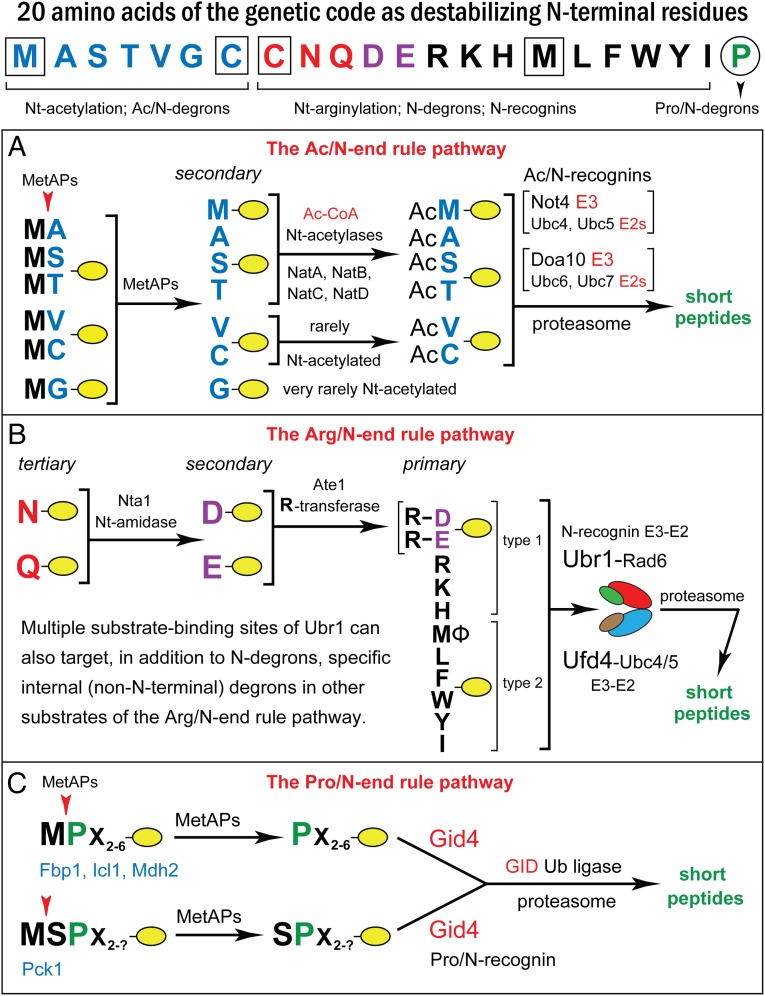
Fig. 1.
The N-end rule pathways. N-terminal residues at the top of the diagram are indicated by single-letter abbreviations. Twenty DNA-encoded amino acids are arranged to delineate three sets of N-degrons in S. cerevisiae, corresponding to three N-end rule pathways. N-terminal Met is cited twice, because it can be recognized by the Ac/N-end rule pathway (as Nt-acetylated N-terminal Met) and by the Arg/N-end rule pathway (as unacetylated N-terminal Met). N-terminal Cys is also cited twice, because it can be recognized by the Ac/N-end rule pathway (as Nt-acetylated Cys) and by the Arg/N-end rule pathway (as an oxidized, Nt-arginylatable N-terminal Cys, denoted as Cys* and formed in multicellular eukaryotes but apparently not in unstressed S. cerevisiae). (A) The Ac/N-end Rule pathway. (B) The Arg/N-end rule pathway. (C) The Pro/N-end rule pathway. See the Introduction for references and brief descriptions of these pathways.