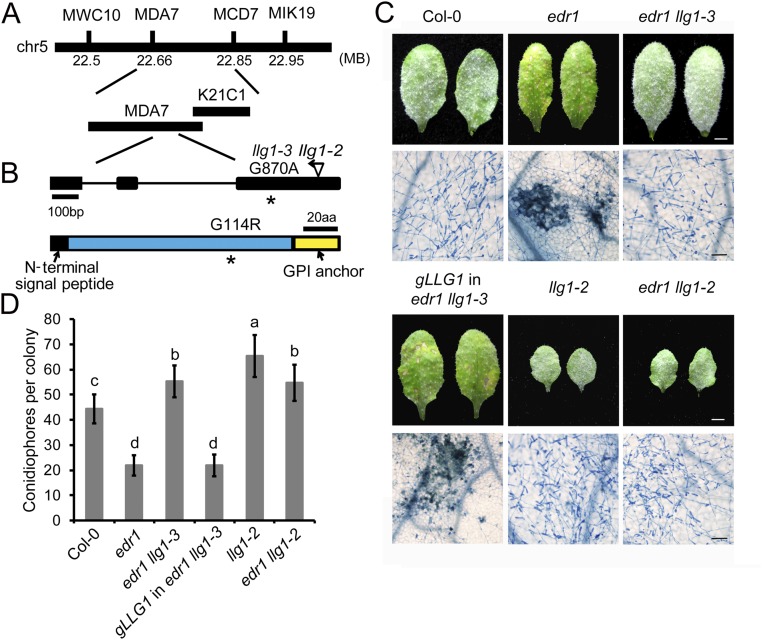
Fig. S2.
Map-based cloning of llg1-3. (A) Map position of the llg1-3 mutation. Markers and BAC clones are indicated. (B) Gene structure of LLG1. The asterisk indicates the point mutation in the llg1-3 allele. The insertion position of the previously identified llg1-2 T-DNA allele is shown. Exons are indicated by black boxes and introns are indicated by lines. The LLG1 protein contains an N-terminal signal peptide and a C-terminal anchor signal. The mutation in llg1-3 causes a G to A point mutation, resulting an amino acid change from Gly to Arg. aa, amino acids. (C) Four-week-old plants were inoculated with G. cichoracearum. Photos were taken of leaves of Col-0, edr1, llg1-2, edr1 llg1-2, edr1 llg1-3, and a representative LLG1 edr1 llg1-3 complementation line at 7 dpi. The infected leaves were stained with Trypan blue to show fungal structures and dead plant cells. (Scale bars, 0.25 cm for white; 100 μm for black.) (D) Quantitative analysis of conidiophore formation at 5 dpi. Error bars represent SD of three independent experiments (n = 25). Lowercase letters represent statistically significant differences (P < 0.05, nested ANOVA).