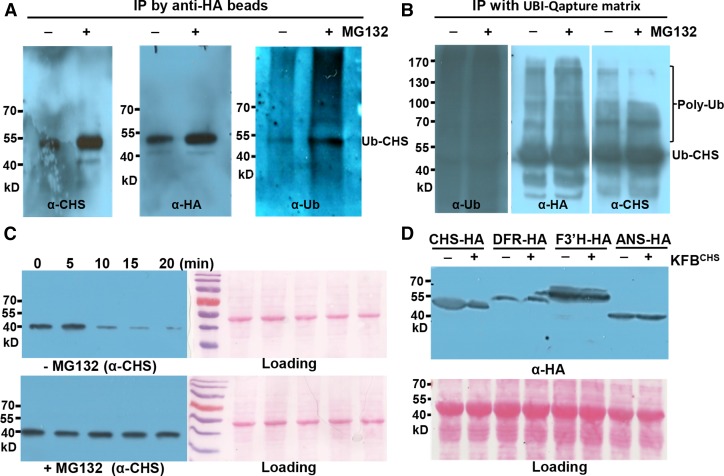
Figure 2.
CHS Protein Is Subject to Ubiquitination and 26S Proteasome-Mediated Degradation.
(A) Detection of the ubiquitinated AtCHS-HA proteins. Transiently expressed AtCHS-HA was IP-enriched by anti-HA beads from tobacco leaves in the presence or absence of 50 μM MG132 and detected with anti-AtCHS (left), anti-HA (middle), and antiubiquitin antibodies (right), respectively. The images of original blots with full molecular markers are presented in Supplemental Figure 4.
(B) Enrichment of the ubiquitinated CHS-HA proteins. Total ubiquitinated proteins were enriched by ubiquitin affinity binding matrix (UBI-Qapture matrix) from tobacco leaves with transiently expressed AtCHS-HA and preinfiltrated with or without 40 μM MG132. The enriched proteins were then detected with antiubiquitin (left), anti-HA (middle), and anti-AtCHS (right) antibodies, respectively; the smear/bands above the primary ubiquitinated CHS (Ub-CHS) band represent the polyubiquitinated CHS species (Poly-Ub).
(C) Cell-free degradation of the endogenous CHS enzyme from Arabidopsis. Total proteins from 5-DAG Arabidopsis seedlings were incubated in the degradation buffer at 37°C in the presence or absence of 50 μM MG132. At the indicated time points, the level of CHS protein was monitored by immunoblot using anti-AtCHS antibody. Ponceau S staining serves as the loading control for the amount of total protein.
(D) Immunoblots with anti-HA antibody for AtCHS-HA, AtDFR-HA, AtF3′H-HA, and AtANS-HA fusion proteins coexpressed with KFBCHS (pGWB402-KFBCHS) or the empty vector (pGWB402) in tobacco leaves. Ponceau S staining serves as the loading control for the amount of total proteins. Note that both AtCHS-HA and AtDFR-HA exhibited the larger molecular sizes than their predicted molecular masses.