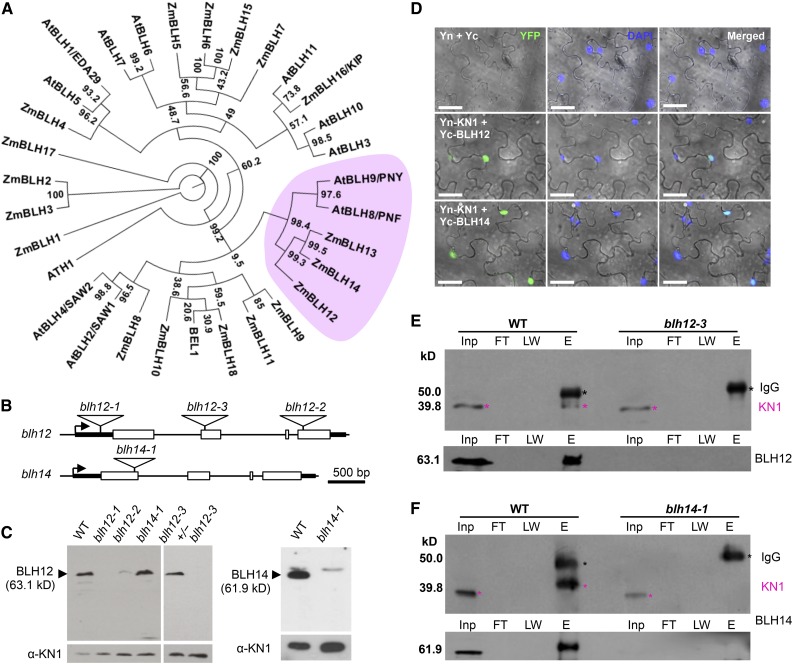
Figure 1.
Maize PNY Homologs BLH12 and BLH14 Interact with KN1.
(A) A phylogenic tree of maize and Arabidopsis BLH proteins. The PNY clade is pink. Bootstrap values are indicated at each branch point. Gene IDs and accession numbers are listed in Supplemental Table 3. The alignments used to generate the phylogeny are provided in Supplemental File 1.
(B) Mutator insertions in blh12 and blh14. Boxes, triangles, arrows, and thick lines indicate exons, Mutator transposons, transcription start sites, and 5′ or 3′ untranslated regions, respectively. Thin lines represent other regions including up- and downstream regions and introns.
(C) Immunoblots for BLH12 (left) and BLH14 (right) using protein extracts from shoot apices of 3-week-old seedlings. KN1 was used as a loading control (bottom). WT, wild type.
(D) BiFC assay showing interactions between KN1 and BLH12 or BLH14 in planta. Agrobacterium tumefaciens lines containing constructs shown on the left were infiltrated into N. benthamiana leaves. Three biological replicates (∼100 nuclei for each replicate) were observed and fluorescence was detected in ∼25% of nuclei. Confocal images were overlaid on the bright field. Yn and Yc represent YFP N-terminal half and C-terminal half, respectively. Bars = 40 µm.
(E) and (F) Protein coimmunoprecipitation of KN1 with BLH12 (E) or BLH14 (F). Protein extracts from shoot apices were immunoprecipitated using anti-BLH12 or anti-BLH14 antibodies followed by immunoblots using anti-KN1 (top), anti-BLH12 (bottom in [E]), or anti-BLH14 (bottom in [F]) antibodies. Black and magenta asterisks indicate IgG heavy chains and KN1, respectively. KN1 immunoprecipitated with BLH14 runs at a higher molecular weight, possibly due to posttranslational modifications. Inp, total inputs. FT, flow-through fractions; LW, washing fractions; E, eluted fractions.