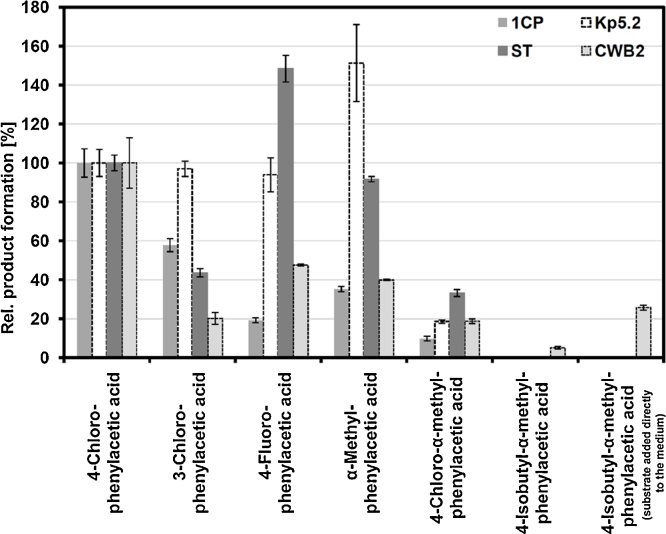
Fig. 3.
Substrate specificities of strains ST, Kp5.2, 1CP, and CWB2 for the conversion of substituted styrenes into the corresponding phenylacetic acids.
Pseudomonas fluorescens ST (0.61 mgcdw ml−1), Sphingopyxis sp. Kp5.2 (1.0 mgcdw ml−1), Rhodococcus opacus 1CP (0.98 mgcdw ml−1), and Gordonia sp. CWB2 (1.9 mgcdw ml−1) were cultivated for 12 h in the presence of 25 μmol substrate as described in the Section 2. If not otherwise stated, the substrate was provided via gas phase. The product yields obtained during a period of 12 h were referred to the cell dry weight and normalized towards 4-chlorophenylacetic acid formation (=100%). Mean values and standard errors of three to four independent measurements are given. 100% rel. yields correspond to: strain ST: 520 ± 21 μmol gcdw−1; strain Kp5.2: 98.2 ± 6.9 μmol gcdw−1; strain CWB2: 67.7 ± 8.8 μmol gcdw−1; strain 1CP: 27.9 ± 2.0 μmol gcdw−1.